Fortune 500 Brands & Corporate Foundations Extend Over $54 Million in Capital Commitments with Closed Loop Partners
June 30, 2020
Investment will support urgent need for additional recycling infrastructure and the development of end markets, keeping valuable materials in circulation across the U.S.
New York, NY — Closed Loop Partners today announced that some of the world’s largest consumer brands and corporate foundations are extending more than $54 million in capital commitments with the Closed Loop Infrastructure Fund (CLIF). This extension is testament to the progress CLIF has made over the last five years toward building a more circular economy and the sense of urgency from these brands to accelerate their circular economy goals and support the transformation of the recycling system.
Today, the original nine investors in the fund – 3M, Coca-Cola, Colgate Palmolive, Johnson & Johnson Consumer Health, Keurig Dr. Pepper, PepsiCo, Procter & Gamble, Unilever and The Walmart Foundation – are extending their capital commitments, strengthening their investment in the infrastructure needed to build a more circular economy. Amazon, Danone North America, Danone Waters of America, Nestlé Waters North America and Starbucks have since joined the fund. Together, these companies’ major investments support additional recycling infrastructure and spur growth and technological innovation around end markets for post-consumer materials across North America. No company will be able to address the issue of plastic waste alone, and we need the industry to collectively work together to accelerate circular supply chains and keep materials in play.
With a global pandemic, growing climate risks and increasingly tighter municipal budgets, continued investment is critical to build our recovery infrastructure and economy back in a way that builds good job opportunities and safe and robust recovery systems to manage the critical inputs to product and packaging supply chains. And today, these brands show their shared commitment toward building back better and creating more efficient and effective systems to turn their product and packaging waste back into the inputs to future manufacturing.
The corporate investors in the Closed Loop Infrastructure Fund have proven the value created from investing in the circular economy. We invite other companies, brands and investors to join these industry leaders by investing with us in the infrastructure and technology needed to keep materials in manufacturing supply chains and out of landfills and marine environments – Ron Gonen, CEO of Closed Loop Partners.
The initial investment from these brands has already leveraged more than $200 million in co-investment, supporting the development of domestic recycling infrastructure, local jobs and new markets in cities across the country, including:
- Eureka Recycling, Minneapolis, Minnesota: A locally operated nonprofit social enterprise, Eureka recovers nearly 100,000 tons of primarily residential recycling per year. This diverts valuable material from the incinerator or landfill and protects the health and environment of the local community. Eureka prides itself on its best-in-class operation, producing high quality material; the facility has one of the lowest contamination rates in the country. Eighty percent of the facility’s material stays in Minnesota and ninety percent in the Midwest, further spurring local growth. Eureka Recycling works everyday to demonstrate that waste is preventable not inevitable.
- Emerald Coast Utilities Authority (ECUA), Florida: Since building its own state-of-the-art single stream facility, the ECUA materials recovery facility has become an asset for a region that had not previously had a long-term or reliable solution for processing recyclables. The facility generates economic benefits in the form of avoided tipping fees and revenue from commodity sales. For the 21-month period starting in January 2017, the facility generated $4.2 million in economic benefits. To date, the facility has operated at a profit margin between 10% and 30%, which gives ECUA capital to invest in other critical water, sewage, and solid waste infrastructure and programs.
- TemperPack, Virginia: On the forefront of materials science innovation, TemperPack manufactures proprietary plant and fiber-based insulated packaging solutions for cold chain shipments, perishable food and pharmaceuticals. Their products replace the need for styrofoam, a type of plastic that contaminates recycling facilities. Instead, TemperPack’s solutions are certified curbside recyclable, bringing value to recovery systems across the U.S. as their materials are kept in circulation.
Today’s reinvestment announcement builds on the success of these projects and will fund similar projects to accelerate and build circular supply chains. Thirty-seven of the world’s largest consumer brands and retailers, including many of those fueling this investment, have made public commitments to use recycled plastics in their packaging within the next ten years. This signals the opportunity to shift billions of dollars from the “take, make, waste” linear supply chain to circular supply chains. Current projections indicate new real demand of 5 million to 7.5 million metric tons of recycled content by 2030, requiring an increase of supply of 200-300%. It will only be possible to meet this need through greater collective investment from brands to move technology along faster.
Brands and investors interested in learning more about CLIF or getting involved should contact [email protected].
Quotes from Our Investors
By connecting the dots across the entire value chain, Closed Loop Partners is committed to keeping valuable materials in play. With our ambitious goals around recyclability in practice and at scale, as well as the use of recycled content in our products, we need companies like Closed Loop Partners to continue to increase the efficiency of supply chains so that we can access more recycled content. The demand is there, but the supply side needs investment and that’s why we’re reinvesting our capital with Closed Loop Partners. Let’s continue the good work! – Ann Tracy, CSO, Colgate Palmolive
Keurig Dr Pepper’s business is fueled by the power of partnerships which we use to drive positive impact. We signed on as original investors in Closed Loop Partners’ Infrastructure Fund to address waste and pollution in North America. As the waste system and potential solutions continue to evolve, there is still work to be done. Today we are recommitting to the important work being done by CLP and our co-investors by reinvesting in the Infrastructure Fund and continuing to strengthen domestic recycling capacity and technology across the country – Monique Oxender, Chief Sustainability Officer, Keurig Dr Pepper
We joined the Closed Loop Investment Fund as a founding member because it is an innovative impact investment opportunity that we believe will increase access to recycling infrastructure across the U.S. Based on the rigorous performance criteria for the Fund, it has been a wise investment decision for our company and we have decided to reinvest for another five-year term. The Fund has shown how industry leaders can come together to advance the circular economy and create a more sustainable future – Paulette Frank, VP, Environmental Health, Safety & Sustainability, Johnson & Johnson
At 3M, Science for Circular is one of our top sustainability priorities and we are committed to advancing design solutions that do more with less material. To reach our targets and promote a global circular economy, we need to ensure recycled materials are widely available. Closed Loop Partners is on the front lines of this work and their investment in recycling facilities across the country has driven much needed growth. We are proud of our continued collaboration and aim to build on the momentum we are seeing in the recycling sector to create a better future – Gayle Schueller, Vice President and Chief Sustainability Officer, 3M
At Coca-Cola we care about the environment and the natural resources we all share. That’s why we set a global goal to collect and recycle the equivalent of every bottle or can we sell globally by 2030. We know we can’t reach this goal without significant partners like the Closed Loop Fund who are helping to address the gaps in the domestic recycling system. We’re excited to continue our investment in the Closed Loop Fund and support their meaningful progress to optimize and upgrade recycling infrastructure as we work to realize our vision for a World Without Waste – Bruce Karas, Vice President, Safety and Sustainability, Coca-Cola North America
At PepsiCo, we’re striving to build a world where plastic need never become waste by reducing, recycling and reinventing our packaging. But we know we can’t do it alone. Through our investment in Closed Loop Partners’ Infrastructure Fund, recycling facilities across the country are being improved, helping give new life to materials and driving sustainable change. We are committed to building a circular future for packaging and know that impact at scale requires partnerships like this – Tim Carey, Vice President of Sustainability, PepsiCo Beverages North America
Now more than ever we are committed to making a positive impact on society and the environment. Strengthening and developing recycling infrastructure across North America is a critical part of this. Closed Loop Partners’ investment track record proves that investing in the development of the circular economy is not only environmentally beneficial but also good for the economic recovery. Increased access to recycling creates thriving communities, spurring innovation in end markets, getting materials back into supply chains for reuse and creating a healthier environment – Virginie Helias, Chief Sustainability Officer, Procter & Gamble
Our plastics commitments include halving our use of virgin plastic and collecting and processing more plastic than we sell by 2025. Investing in recycling infrastructure is key to both of these goals, and Closed Loop Partners helps make it possible to support a circular economy for plastics. Our vision is a world where everyone works together to keep plastic within the circular economy and out of the environment – Viviana Alvarez, Head of Sustainability for Unilever North America
The plastics value chain needs to be rewired for circularity, and innovation and infrastructure investments are needed to seriously address the plastic waste issue in the United States. We are proud to be a lead investor in the Closed Loop Infrastructure Fund to continue to advance waste reduction solutions in communities across the country – Chelsea Scantlan, Senior Program Officer, The Walmart Foundation
About Closed Loop Partners
Closed Loop Partners is a New York based investment firm comprised of venture capital, growth equity, private equity, project finance and an innovation center. The firm invests in the circular economy, a new economic model focused on a profitable and sustainable future. In 2014, Closed Loop Partners established the Closed Loop Infrastructure Fund (CLIF) that provides zero interest and below market rate loans to companies and municipalities building recycling and circular economy infrastructure in North America. Investors in CLIF include Amazon, 3M, Coca-Cola, Colgate Palmolive, Danone North America, Danone Waters of America, Johnson & Johnson Consumer Health, Keurig Dr. Pepper, Nestlé Waters North America, PepsiCo, Procter & Gamble, Starbucks, Unilever and The Walmart Foundation. Learn more at www.closedlooppartners.com.
Bringing NextGen Cups to Market: It Takes a Village
June 29, 2020
The NextGen Consortium is a global initiative convened by Closed Loop Partners’ Center for the Circular Economy. Starbucks and McDonald’s are founding partners of the Consortium, together with supporting partners The Coca-Cola Company, Yum! Brands, Nestlé and Wendy’s, as well as WWF as an advisory partner. IDEO is the Consortium’s innovation partner.
Local cafes, cities and students joined the NextGen Consortium’s collaborative efforts to advance reusable, recyclable and compostable cup solutions in pilots across the San Francisco Bay Area earlier this year.
Two years ago, the NextGen Consortium asked innovators: “How might we design the next generation fiber cup to be recoverable on a global scale, while maintaining the performance standards we know and trust?” From the start, we knew that our ability to successfully address the systemic challenge of cup waste would require strong collaboration across the entire cup ecosystem – from brands, suppliers and innovators, to municipalities, materials recovery facilities and mills, to advocacy groups and nonprofits, to the broader public. And we’ve been collaborating with these essential stakeholders, and others, ever since.
The NextGen Consortium serves as a collaborative platform for larger brands looking to move the needle on sustainability. By working together we’re one step closer to finding long term solutions, quicker than we would on our own — Jessica Marshall, Sustainability at McDonald’s
The Consortium’s journey began with the NextGen Cup Challenge —an open call for sustainable cup solutions that resulted in nearly 500 submissions from more than 50 countries. Twelve Cup Challenge winners were given the opportunity to enter the NextGen Circular Business Accelerator or the Advanced Solutions cohort; programs aimed at further developing the select winning cup companies – bringing them closer to pilot and market-readiness. And in early 2020 we launched The NextGen Pilot Readiness Program, a series of live, in-market pilots in the San Francisco Bay Area to further test and refine promising reusable and single-use solutions in surrounding local cafes.
We’re excited to keep learning, testing and exploring new cup technologies with the NextGen Consortium. The collaboration between companies, innovators and stakeholders is critical in our journey to find, and bring to scale, a more sustainable cup. — Chris McFarlane, Project Manager at Starbucks
NextGen Pilot Teams
●CupClub: A returnable cup ecosystem, providing a service for drinks. Think bike sharing, but for cups.
●Muuse : A deposit-based platform for smart, reusable beverage packaging, connecting their cups—and third party products—to Internet of Things technologies.
● Footprint: Fully formed fiber-based cups, lids and straws with an aqueous-based coating that is recyclable and compostable.
●PTT MCC Biochem: Recyclable cups with an innovative, bio-based BioPBS™ coating that makes the cup certified for compost in an industrial compost facility.
The Consortium’s pilots took place across multiple clusters of local cafes in San Francisco, Palo Alto, and Oakland. We evaluated cups and cup systems on their technical feasibility, business viability, user desirability, and systemic circularity. And, through it all, the collaborative spirit came to the fore as the critical ingredient for success.
Tackling a challenge as complex and massive as global cup waste requires a multitude of stakeholders—and it’s important to activate them from the start in order to advance the entire ecosystem. The pilots’ success hinged on collaborative municipalities (San Francisco, Palo Alto, Oakland), local neighborhood associations and universities eager to drive awareness, willing and excited local cafes to help establish a network effect of pick up and drop-off points, curious customers to experiment with new habits and an engaged media to drive awareness. After engaging all of these stakeholders and putting the cups to the test in local cafes, what did we learn?
Customer and Barista Insights Drive Rapid Iterations
Every minute counts when it comes to encouraging the uptake of reusable cup systems. And every user engagement offers a valuable opportunity for feedback. Customers have to sign up to a mobile app to log their cup, navigate the payment process, receive their beverage and ultimately return their cup to either a cafe or a drop-off point. Each step of this journey impacts their perception of reusable cups. For example, customer satisfaction was higher when there was a lost cup fee rather than an upfront deposit, and customers breathed easy after an alert confirmed a successful cup return. Similarly, baristas provided vital feedback. Even a simple verbal prompt asking customers whether they’d “like their order in a reusable cup” increased interest and engagement. These insights, alongside the experimentation mindset that characterized the pilots, enabled teams to rapidly prototype and improve according to key learnings.

Different Local Cafes Banded Together to form Clusters for the Pilots
Clusters are areas where 5 or more stores are located within a 5-minute walk. This walk, or the “pedestrian shed,” is considered the distance people are willing to walk before opting to use transit instead. Cup drop-off points work best when along a customer’s existing route. Local cafes including Coupa Cafe, Verve Coffee Roasters, Andytown, and Equator Coffees formed clusters, opened up their retail locations and helped lay the groundwork for the Pilot rollouts. During the pilots we saw some cups distributed at one cafe and returned to another. To hit a critical mass of users and truly scale reusable cup systems, support for this kind of behavior is imperative. It is also highly complex and requires honing and thoughtful planning as well as collaboration across multiple brands.
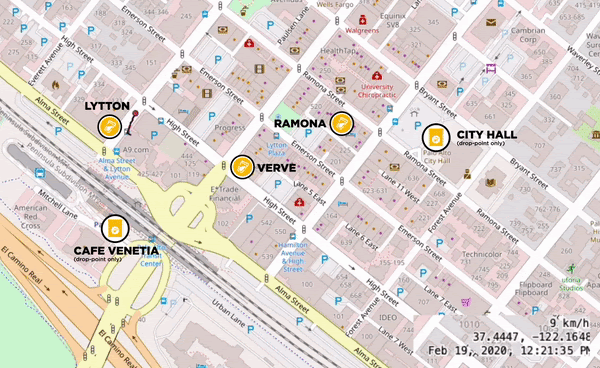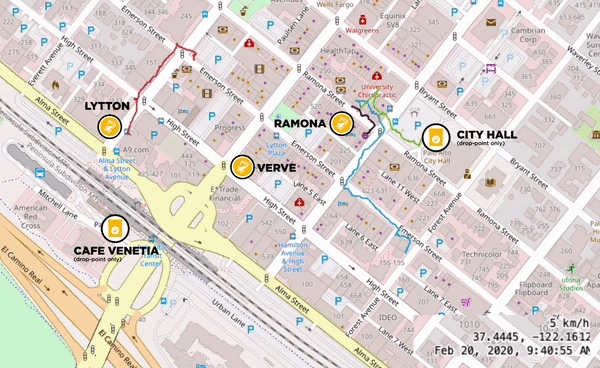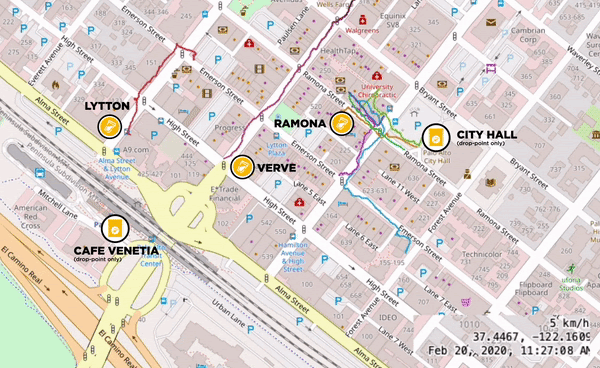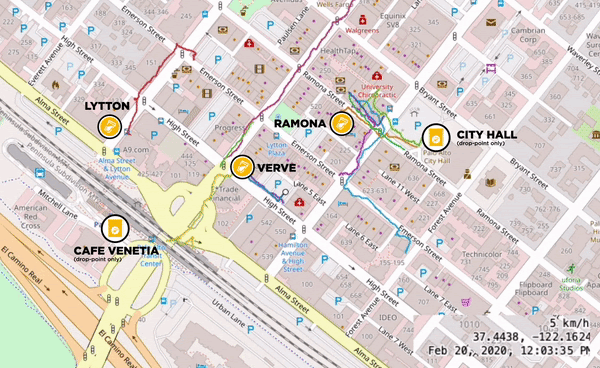
A cluster of local cafes and drop-off points
City Governments, Universities and NGOs Played a Critical Role in Galvanizing Momentum
Usership, especially early on, is directly tied to awareness. Data is most informative at higher volumes. The City of Palo Alto’s Zero Waste team was instrumental in identifying retail partners for the Pilot and educating their network, including zero waste leads in neighborhoods, about the pilots. The City of San Francisco’s Department of the Environment team was also engaged and eager to learn more about reusable cup solutions, especially in the face of proposed regulations and ordinances. The non-profit organization UPSTREAM made key introductions to city officials and shared essential information regarding upcoming ordinances and policies. The network effect is real. By engaging these organizations and their respective communities, our reach multiplied, attracting more pilot participants, thus gathering more data to optimize systems and prepare for the mass market.
The success of the pilots was built on the foundations of collaboration, which engaged diverse stakeholders and enabled agile and quick responses to feedback. COVID-19 brought unforeseen challenges and intensified the question, how can we maintain customer trust with reusable cups? Throughout the pilots, the reusable solutions adhered to rigorous washing protocols, including one team utilizing an off-site industrial facility to ensure the strictest hygiene standards were maintained. The pandemic has further emphasized the importance of sanitation and health, and the critical need to communicate these elements effectively to customers.
Moving forward, collaboration among diverse stakeholders is essential to ensure that innovative new systems of consumption can bring convenience and delight, while reducing the environmental footprint of our daily habits. The NextGen Consortium will continue to work with the Cup Challenge winners, as well as other promising cup innovations, to advance their solutions, while simultaneously strengthening and building the cup recovery ecosystem as a whole. This includes exploring new processes and working with waste collectors, materials recovery facilities, municipalities, and paper mills, among others, to explore the opportunities around cup recycling and composting. Our pilots in the San Francisco Bay Area provided invaluable feedback on how we can collectively enhance the drinking experience in a way that stakeholders (and the environment) can feel good about. And we’re excited to continue to accelerate the future of more sustainable cups.
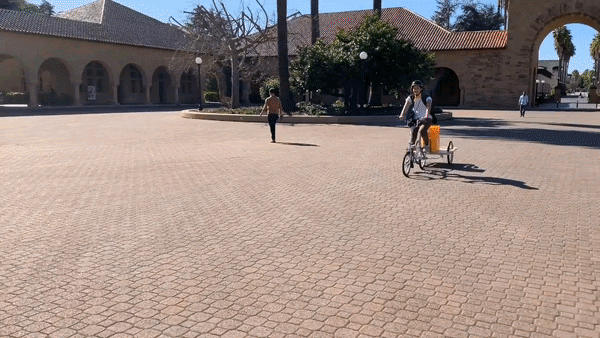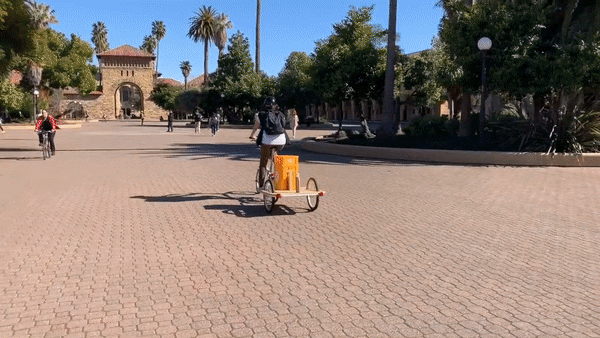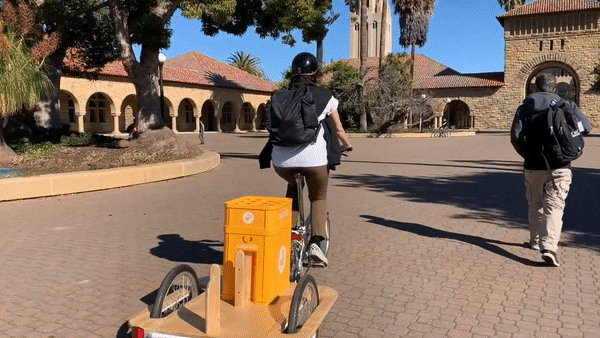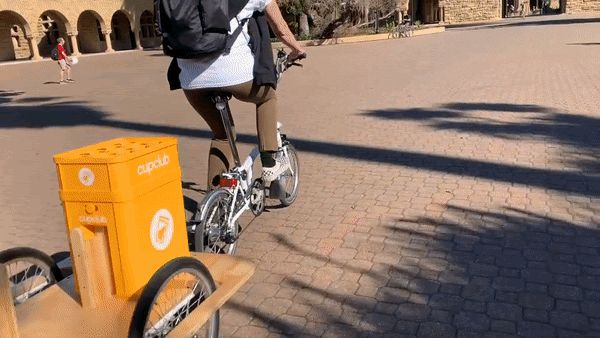
CupClub’s Cup Chariot in action on Stanford University’s campus
Circular Innovations for an Evolving Retail World
June 28, 2020
This article first appeared here on the Retail Industry Leaders Association’s blog.
At Closed Loop Partners we believe it is disruptive circular solutions that provide resilience and create unique opportunities in the face of global pandemics, the ocean plastics crisis and accelerating climate risks. But we don’t need to start from square one. The transition to a circular economy that aligns the interests of shareholders, customers, local communities and the environment is already underway. Circular solutions maximize retailers’ opportunities for resource efficiency and profit, while aligning with consumer demand and long-term sustainability. So how do we get there?
HARNESS INNOVATION TO STOP WASTE BEFORE IT HAPPENS
The future of retail is arriving faster than anticipated. During the pandemic, trends like home delivery and automated check out accelerated, while the consequences of excess inventory became costly. The four key drivers of the circular economy – transparency, digitization, automation and localization – suddenly aligned with the urgent need to safely and efficiently deliver goods. The failings of our current opaque global supply chains reinforce that innovations in digitizing inventory and sharing data can create efficiencies and prevent waste, opening up new possibilities for smart stocking, real time tracking and optimized reverse logistics for returns.

THINK OUTSIDE THE BOX AND REEXAMINE TRADITIONAL BUSINESS MODELS
Circular business models are reimagining the relationship between producer and customer. Nowhere is this more apparent than in fashion, where rental models and recommerce are growing their market share rapidly. This is critical as fashion consumption continues to increase, while the average number of times a garment is worn in its lifetime decreases. Between 2000 and 2015, the EPA noted that textile waste by weight jumped 67%. But profitable alternatives to throwing these valuable resources away have already emerged. Apparel leasing in the U.S. is estimated to reach a market value of $4.4 billion by 2028, while the sale of second-hand clothing is expected to more than double to $51 billion by 2023 according to GlobalData and ThredUp. Companies like The Renewal Workshop operating apparel refurbishment services for brands’ damaged or used goods, enabling brands to sell previously unsellable inventory. Both approaches offer traditional retailers opportunities for additional revenue streams from existing stock, increasing customer touchpoints with individual companies while encouraging long-term brand loyalty and customer satisfaction. This breaks the cycle of waste and helps brands recover the full value of products they’ve already manufactured.

Clothing from The Renewal Workshop
ACCELERATE ADVANCED RECYCLING TECHNOLOGIES TO KEEP EXISTING VALUABLE MATERIALS IN PLAY
After a product’s resale market/value has been exhausted, there is still value to be found. Today’s ‘waste’ stream is rapidly evolving as new types of packaging and textiles enter the market. Most of these new formats and material blends are difficult to recycle after use, and few end markets exist for the materials to profitably remain in the value chain. But game-changing advanced recycling technologies are expanding. These technologies clean or break down mixed plastic packaging and synthetic fibers into their original building blocks so that they can then be reincorporated into manufacturing supply chains without diminished quality. Advanced recycling companies like Evrnu convert textile waste into new, high quality fiber for the creation of new clothing, in partnership with brands and retailers. It is this combination of disruptive technologies and collaboration across the entire value chain that can help eliminate the costs of incineration and landfill disposal, and instead create revenue from recycled materials.
It’s always the right time to reduce costs, increase efficiency, and protect the environment we share. Now is the moment to embed circular principles into core business models and harness these emerging innovations to ensure a more prosperous and sustainable future.
Closed Loop Partners at the United States Senate Environment and Public Works Committee on Recycling
June 19, 2020
Launched in 2014, Closed Loop Partners (CLP) is the first investment firm primarily focused on building the circular economy. Our vision is to help build a new economic model focused on a profitable and sustainable future that aligns the interests of shareholders, brands and local communities and the environment that we all share. Closed Loop Partners provides equity and project finance to scale products, services and infrastructure at the forefront of the development of a circular economy. We have over the past 5 years built a development system that connects entrepreneurs, industry experts, global consumer goods companies, retailers, financial institutions and municipalities.
On June 17, 2020, Bridget Croke, Managing Director, at Closed Loop Partners spoke at the United States Senate Environment and Public Works Committee as they held a hearing on “Responding to the Challenges Facing Recycling in the United States.” The following text is drawn from her testimony.
Today, we have over 40 investments in companies and municipal projects in the United States, all focused on helping Americans avoid landfill disposal fees while generating good jobs in the recycling and manufacturing sector. Our investors are a combination of some of the largest American based consumer brands in the world including 3M, Coca-Cola, Colgate Palmolive, Johnson & Johnson, Keurig Dr. Pepper, PepsiCo, Procter & Gamble, Unilever and The Walmart Foundation, as well as the American Beverage Association, institutional investors, family offices and environmental foundations. CLP proves that public–private partnerships are critical to unlocking the capital needed to build robust recycling and circular economy infrastructure needed to create jobs, reduce waste and build the supply chains of the future.
Despite some of the headlines we’ve all seen, recycling is big business in America and should create the manufacturing feedstock for future packaging. In 2019, the recycling industry in America generated over $110 billion in economic activity, $13 billion in federal, state, and local tax revenue and 530,000 jobs. In spite of COVID and market challenges in recent years, 2020 is shaping up to be a year of major innovations in the recycling industry as it becomes central to circular economy business models that major consumer goods companies and cities are deploying. Transitioning US manufacturing to circular supply chains could unlock a $2 trillion opportunity.
Recycling continues to be the most cost-effective option for the vast majority of American cities. The economics are simple. Cities have two choices when it comes to disposal: recycle or landfill. While the value of recycling is generally reported as the amount that a city can be paid for its recyclables, the core economic value of recycling is actually the opportunity for a city to avoid costly landfill disposal fees. Economic analysis conducted has shown that the U.S. scrap recycling industry is a major economic engine powerful enough to create 531,510 jobs and generate $12.9B in tax revenue for governments across the US.
New York City, the largest market in the United States, is an example of how advanced recycling infrastructure and strong local markets create long term profits. New York City has a long-term public-private partnership with Pratt Industries that converts all of its recycled paper locally into new paper products sold back into the NYC market. Via its contract with Pratt, New York City is paid for every ton of paper its residents recycle, as opposed to a cost of over $100 per ton to send paper, plastics and metals to a landfill.
Minneapolis is another good example. Eureka Recycling and the City of Minneapolis invested in local community outreach focused on keeping their recycling stream clean of contamination, defined as non-recyclable material. The result is one of the lowest contamination rates of any municipal recycling program in the country. With a clean stream of valuable recyclables, Eureka consistently shares with Minneapolis the profits earned from the sale of their recyclables. In many other cities, unfortunately, approximately 15% of the material that arrives at the municipal recycling facility is considered contamination. Municipal recycling programs that keep contaminants out of the recycling stream via strong community outreach or enforcement realize lower costs and better revenue opportunities. Municipalities that recognize that recycling is part of the commodities industry, not the waste industry, generate value.
Along with the examples of Pratt Industries in New York City and Eureka Recycling in Minneapolis, Recology in San Francisco and Balcones in Austin, among others, continue to provide their municipal and commercial customers robust recycling service. In addition, municipalities like Pensacola, Florida and Davenport, Iowa that manage their own best in class recycling facilities consistently reduce landfill disposal costs and create local economic value for their constituents.
The value of recyclable commodities continues to have a wide range. The cost to process municipal recyclables at a recycling facility is, on average, $70 per ton. That means that for a recyclable commodity to have value, it must have a market that pays the recycling facility over $70 per ton of that material. A sample of the commodities that are usually profitable to recycle include PET plastic (beverage containers), HPDE plastic (laundry detergent and soap containers), rigid polypropylene (bottle caps, some yogurt containers), cardboard and aluminum.
In 2020, three innovations are driving the increased profit potential of recycling in America and the development of a vibrant and growing Circular Economy.
- The introduction of robotics and artificial intelligence. The future of the industry will be led by the recycling facilities that produce the highest quality commodity bales of materials. Companies like AMP Robotics have introduced robotics (robots) with artificial intelligence systems that enable the sorting and production of high-quality commodity bales, supply chain tracking and safeguards against contamination that were never before imagined in the industry.
- Packaging innovation. We are seeing the emergence and growth of smart refillable packaging systems like Algramo that makes it cheaper and more convenient for consumers to use packaging more than one time. We are also seeing a growth in packaging that is designed to be recycled for value. Temperpack, for example, is a packaging technology that uses recycled cardboard to keep packaged food cold, replacing a significant amount of low value plastics like Styrofoam peanuts, which are both not recyclable and a common contaminant in the recycling system.
- Advanced plastics recycling technologies, including purification technologies and chemical recycling technologies. Purification is an enzymatic process that improves the quality of recycled plastics so they can more easily be used again in packaging. P&G invented a technology and helped launch a company, PureCycle Technologies, that will significantly increase the value of recycled plastic by removing color and smells. Chemical recycling is a process whereby plastic is depolymerized back to the base monomer, intermediary or carbon state in order to remanufacture a new plastic. Some plastics, like PET, HDPE and rigid polypropylene have significant value and are very profitable for the recycling industry, but they can degrade after a number of recycling cycles while some other plastics currently have limited value or are challenging to recycle. Chemical recycling has the potential to create an infinite circular economy value loop for all plastics. Some of the leading innovators are backed by major consumer goods companies. In 2020, we expect a number of emerging companies to move from pilot to commercialization phase.
These and other circular advancements are attracting significant private capital from leading investors. The industry saw investments from leading investors across asset classes. Google and Sequoia invested in AMP Robotics, Goldman Sachs is now the largest shareholder in Lakeshore Recycling Systems, Citi is largest investor in rPlanet Earth, a bottle-to-bottle plastics recycling facility in California and SJF Ventures invested in TemperPack.
The emerging leadership demonstrated by a number of retailers and consumer brands is driving the growth of the circular economy and improvements in recycling. Leadership means designing products and packaging that are free of any non-recyclable material and profitable for recycling. These packages are manufactured with recycled content, while reducing raw material inputs. Brands are telling their consumers that their commitment is to use recycled content in their packaging. Leaders are transparent in their progress, reporting in their annual reports the use of different recycled feedstocks. They know that any product or package that is not recyclable is destined for a landfill (or even worse, a river or ocean), and that cost is passed to the taxpayer.
Walmart has developed design for recycling guidelines for their suppliers to ensure the products sold in their stores are recyclable and piloting refillable packaging models. Unilever’s Seventh Generation Brand uses mostly recycled HDPE plastic in its packaging and recycled paper in its paper products. And over 10 global companies have invested over $150m in CLP’s investment funds so together we can help spur more innovation and create more tons of recycled feedstock coming through systems in the US.
We are also seeing a major trend amongst consumer goods companies looking to increase their use of recyclable material in the packaging and products they sell. It makes sense. At scale, along with the considerable environmental benefits, it should be less expensive for companies to manufacture using recycled material. That is why most major beverage companies including Coca-Cola, Keurig Dr. Pepper, PepsiCo, Nestle and Danone as well as the world’s largest consumer goods companies such as P&G, Unilever and Colgate Palmolive are publicly communicating aggressive goals for the use of recycled materials in their products and packaging.
For Americans, recycling is a matter of economic self-interest. Recycling our cardboard, paper, beverage bottles, rigid plastics containers, and aluminum cans has three important outcomes. First, it reduces the cost to manufacture the products we buy. Second, it reduces the amount of our taxpayer dollars used every year to pay landfills. Third, it generates revenue for our communities via the sale of recyclable commodities. A recent analysis reported the average cost to dispose of a ton of municipal waste in the US in 2019 was $55 per ton, and disposal fees in some states average more than $100 per ton.
Despite these economic incentives, large parts of the United States still have little or no recycling collection or processing infrastructure. Much of the economic activity generated by recycling is accomplished by long standing recycling programs on the West and East Coast as well as the upper Mid-West of America. For those who live in parts of the country with limited or no recycling infrastructure, their tax dollars are wasted on the cost of sending valuable commodities to landfill that could otherwise be sold. While the 90m tons currently recycled in the United States saves American taxpayers and businesses over $3 billion annually in landfill disposal fees, over 180 million tons of recyclable materials are landfilled, costing American taxpayers and businesses over $5 billion annually in landfills fees. We are literally throwing money in the garbage.
It is also important to recognize how China, which has received much press as of late for their role in the American recycling ecosystem, impacts the industry. For much of the past 20 years, the U.S. recycling industry was dependent on China as the leading export market. As consumption and waste has increased in China, the Chinese government has decided to develop their own domestic recycling infrastructure. This may cause some short-term pain in some parts of the United States’ recycling industry, but leading companies in the recycling industry, consumer goods and packaging industry, as well as a number of investors, see this as an opportunity to further develop and profit from domestic recycling and manufacturing infrastructure.
These are exciting times in the recycling industry as the development of the circular economy continues to expand. Major innovations are entering the industry ranging from robotics to supply chain mapping to advanced technologies that recycle plastics. Like any major industry analysis in the U.S., there is no one or two cities that should be extrapolated to define the industry. There are cities where recycling is profitable and a major economic engine and there are cities where the recycling program is struggling. What is clear is that the cities that focus on limiting contamination in their recycling program, build efficient and effective material recovery facilities and who contract with best in class recycling companies benefit from recycling programs that are both profitable and produce good local jobs.
Leading municipalities, recyclers, manufactures and brands are starting to partner together to establish, and profit from, a circular economy in the United States where goods are continually manufactured using recycled material from local recycling programs. This partnership in developing a circular economy will result in one of the largest investment opportunities in the United States over the next decade, major reduction in landfill disposal fee paid by municipalities, and become a primary driver of job creation in local economies.
We encourage policy makers to build incentives and develop policy to spur the market for recycled content and product and system innovation that reduces waste, creates jobs and makes recycled content competitive with the raw material market.
4 Companies Addressing Today’s Challenges & Building a Better Future
April 22, 2020

We interviewed four of our portfolio companies’ CEOs to hear how their circular solutions are addressing COVID-19, how their business models are being impacted and what lies in store for the future. Together, they are championing robust, sustainable systems that help to accelerate our transition to a more resilient circular economy.

AMP Robotics: Matanya Horowitz, CEO
AMP is an AI and Robotics company focused on increasing the quantity and quality of sortation processes at recycling facilities.
What are the impacts of COVID-19 on your business today?
Demand for our A.I. sorting technology has significantly accelerated. Our technology directly addresses COVID-19 workplace safety risks, keeping people out of harm’s way, and keeping the public service of recycling going. We’re seeing repeat orders from existing customers and much larger orders from new customers.
How are you keeping people safe while still operating?
As an ‘essential business’, we’ve continued to deploy robots in customer facilities. Logistics are challenging, but we’ve worked closely with our customers to vigilantly adhere to COVID-19 safety protocols.
What developments in the recycling industry will accelerate as a result of COVID-19?
Recycling is vital to the supply chain. This is evidenced as producers race to meet demand for packaging, tissue, and medical supplies. Without recycling there wouldn’t be enough raw materials to keep up. We expect infrastructure investment to increase addressing this vulnerability, while further elevating the importance of recycling.

For Days: Kristy Caylor, CEO
For Days is a direct-to-consumer apparel brand, operating with a fully circular business model.
What does the fashion and apparel industry look like post COVID-19?
Sustainability will be more important than ever before as customers reevaluate their personal priorities and make decisions based both on value and values. Digital sales will continue to grow and there is a good chance we will all be wearing masks for a while…
What are you doing to help frontline workers today?
Over 4 weeks ago, we pivoted manufacturing to make masks based on requests from front line workers. We have been both selling and donating masks and total volume has exceeded 70K masks.
How has your business model been impacted?
We have an authentically optimistic message that is resonating with our community and we are a digitally based business, so that has not changed. Our branded product is doing really well and the mask project has been a big success. We’ve seen strong engagement across all channels and will continue spreading the good vibes!
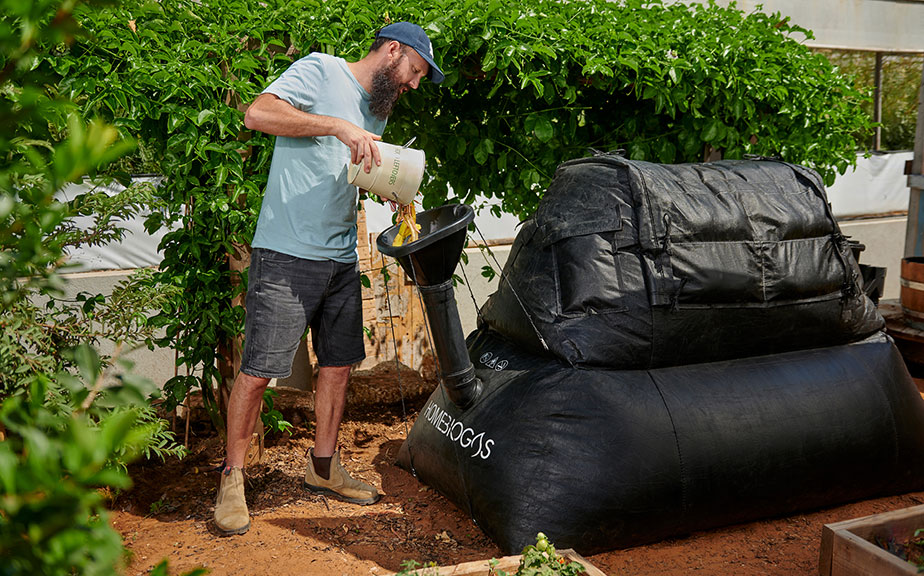

HomeBiogas: Oshik Efrati, CEO
HomeBiogas creates modular household anaerobic digester units that convert household food and yard waste into renewable energy and liquid fertilizer.
Where do you see the most need for HomeBiogas systems?
There are 3 billion people around the world who are still cooking on firewood and charcoal, inhaling toxins from the smoke and suffering from indoor air pollution. Having free and clean cooking gas from HomeBiogas systems would drastically improve and extend the lives of these people.
How does HomeBiogas reduce the risk of disease in emerging markets?
Unfortunately, epidemics and natural disasters will always happen. HomeBiogas systems provide families with independent and reliable access to energy, food security, and sanitation. Families that can make their own fuel and food, and have a solution for waste management will be more resilient and prepared to face challenging times.
What is the change that you would like to see in the world post COVID?
I hope that the world, both governments, and private consumers alike, will wake up to our collective need to take better care of our planet. It’s time we widely adopt green technologies and renewable energies that use the resources we already have like, biogas, solar, wind, rain, etc. COVID showed us that it’s also possible to lessen our impact- we are all capable of consuming less and recycling more. Let’s keep going and keep awareness post-COVID as well.
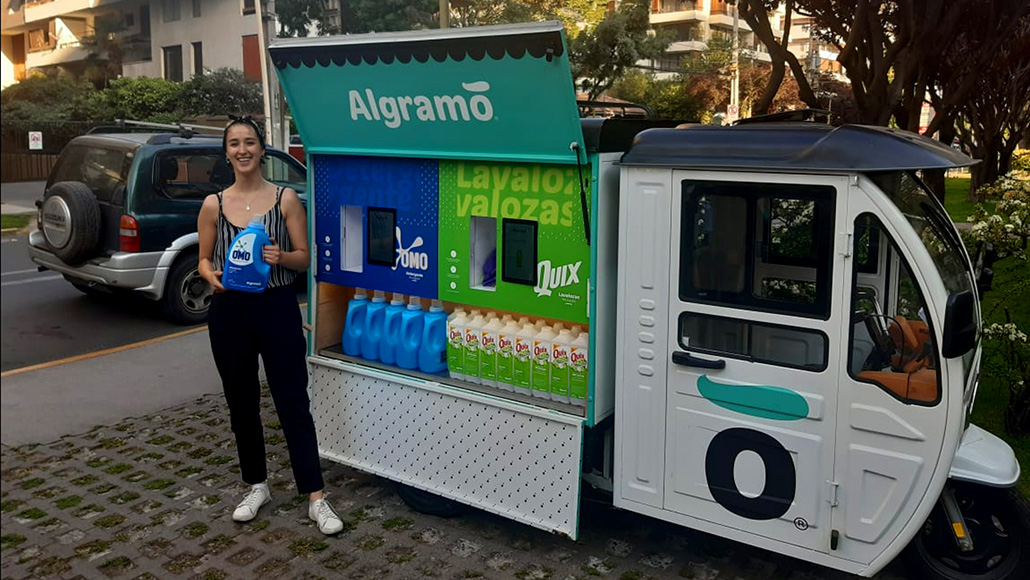

Algramo: José Manuel Moller, CEO
Algramo builds a “smart dispensing system” for CPG products that incentivizes the reuse and refilling of packaging.
What are the impacts of COVID-19 on your business today?
COVID-19 has pushed us to turn our efforts to our delivery system. Our sales in this area have increased since our service allows people to buy essential cleaning products from their homes, reducing any unnecessary exposure to health risks.
How are you keeping people safe while still operating?
We are taking all the necessary measures to take care of our team and our customers. We have protocols in place that promote social distancing and reduce human contact while interacting with our services. Also, we have equipped our sellers with overalls, masks, gloves, hand sanitizer and we clean our tricycles constantly.
What developments in the recycling industry will accelerate as a result of COVID-19?
Recycling services that include home collection are experiencing accelerated growth and so are product refill systems as fewer people touch the containers, therefore reducing the possibility for spreading the virus.
Bringing the NextGen Cup to Life
November 18, 2019

We interviewed four of our portfolio companies’ CEOs to hear how their circular solutions are addressing COVID-19, how their business models are being impacted and what lies in store for the future. Together, they are championing robust, sustainable systems that help to accelerate our transition to a more resilient circular economy.

The NextGen Consortium is working to change the future of beverage consumption. Together, brands, industry experts, and innovators are aiming to bring a waste-free to-go cup to market. With 250 billion fiber to-go cups produced annually, the majority of which end up in landfills today, this is not a small task that one stakeholder can solve alone. And that is the spirit in which the multi-brand NextGen Consortium was formed, launched by Closed Loop Partners in 2018 to advance the design, commercialization, and recovery of sustainable food packaging alternatives.
NextGen Cup is the Consortium’s first initiative, which began with an open call for solutions from around the world to redesign the fiber cup so that it’s fully recoverable at a global scale. Twelve winning teams were selected from the 480 submissions, and six of those teams recently completed an accelerator focused on getting their solutions ready to go to market. The accelerator led to significant progress for each of the teams, as they move along the journey from concept to tangible solution—Accelerator teams have now tested their solutions in a live environment, developed scalable manufacturing plans with 1-3 year rollouts, and have made improvements to their cup design to meet specific circular design criteria.
As we reflect on the learnings of brands, innovators, experts, and designers coming together to tangibly move the needle on a global issue, there are three conditions that have continuously contributed to measurable progress.
AMP Robotics: Matanya Horowitz, CEO
AMP is an AI and Robotics company focused on increasing the quantity and quality of sortation processes at recycling facilities.
What are the impacts of COVID-19 on your business today?
Demand for our A.I. sorting technology has significantly accelerated. Our technology directly addresses COVID-19 workplace safety risks, keeping people out of harm’s way, and keeping the public service of recycling going. We’re seeing repeat orders from existing customers and much larger orders from new customers.
How are you keeping people safe while still operating?
As an ‘essential business’, we’ve continued to deploy robots in customer facilities. Logistics are challenging, but we’ve worked closely with our customers to vigilantly adhere to COVID-19 safety protocols.
What developments in the recycling industry will accelerate as a result of COVID-19?
Recycling is vital to the supply chain. This is evidenced as producers race to meet demand for packaging, tissue, and medical supplies. Without recycling there wouldn’t be enough raw materials to keep up. We expect infrastructure investment to increase addressing this vulnerability, while further elevating the importance of recycling.
For Days: Kristy Caylor, CEO
For Days is a direct-to-consumer apparel brand, operating with a fully circular business model.
What does the fashion and apparel industry look like post COVID-19?
Sustainability will be more important than ever before as customers reevaluate their personal priorities and make decisions based both on value and values. Digital sales will continue to grow and there is a good chance we will all be wearing masks for a while…
What are you doing to help frontline workers today?
Over 4 weeks ago, we pivoted manufacturing to make masks based on requests from front line workers. We have been both selling and donating masks and total volume has exceeded 70K masks.
How has your business model been impacted?
We have an authentically optimistic message that is resonating with our community and we are a digitally based business, so that has not changed. Our branded product is doing really well and the mask project has been a big success. We’ve seen strong engagement across all channels and will continue spreading the good vibes!

HomeBiogas: Oshik Efrati, CEO
HomeBiogas creates modular household anaerobic digester units that convert household food and yard waste into renewable energy and liquid fertilizer.
Where do you see the most need for HomeBiogas systems?
There are 3 billion people around the world who are still cooking on firewood and charcoal, inhaling toxins from the smoke and suffering from indoor air pollution. Having free and clean cooking gas from HomeBiogas systems would drastically improve and extend the lives of these people.
How does HomeBiogas reduce the risk of disease in emerging markets?
Unfortunately, epidemics and natural disasters will always happen. HomeBiogas systems provide families with independent and reliable access to energy, food security, and sanitation. Families that can make their own fuel and food, and have a solution for waste management will be more resilient and prepared to face challenging times.
What is the change that you would like to see in the world post COVID?
I hope that the world, both governments, and private consumers alike, will wake up to our collective need to take better care of our planet. It’s time we widely adopt green technologies and renewable energies that use the resources we already have like, biogas, solar, wind, rain, etc. COVID showed us that it’s also possible to lessen our impact- we are all capable of consuming less and recycling more. Let’s keep going and keep awareness post-COVID as well.

Algramo: José Manuel Moller, CEO
Algramo builds a “smart dispensing system” for CPG products that incentivizes the reuse and refilling of packaging.
What are the impacts of COVID-19 on your business today?
COVID-19 has pushed us to turn our efforts to our delivery system. Our sales in this area have increased since our service allows people to buy essential cleaning products from their homes, reducing any unnecessary exposure to health risks.
How are you keeping people safe while still operating?
We are taking all the necessary measures to take care of our team and our customers. We have protocols in place that promote social distancing and reduce human contact while interacting with our services. Also, we have equipped our sellers with overalls, masks, gloves, hand sanitizer and we clean our tricycles constantly.
What developments in the recycling industry will accelerate as a result of COVID-19?
Recycling services that include home collection are experiencing accelerated growth and so are product refill systems as fewer people touch the containers, therefore reducing the possibility for spreading the virus.
What’s next for the NextGen Cup?
As each of the six teams stepped off the stage during the final accelerator pitch event, the NextGen Consortium entered the next phase of this work: pilot readiness testing.
After the initial prototyping at Google campuses, select teams will now work to increase the size and complexity of their testing locations, looking at universities and offices, among other locations. Additionally, these teams will now begin to prototype alongside select teams from the NextGen Consortium’s “Advanced Solutions Program,” later-stage teams from the NextGen Cup Challenge that did not require the initial accelerator programming. As these teams work to reach market readiness, their greatest need is additional data points that will prove their concept’s ability to operate at scale.
The pilot readiness tests aim to provide much of that data and help setup teams for next steps around scalability. In parallel, the NextGen Consortium will continue its work convening experts and identifying opportunities to align new cup designs and materials with the infrastructure like MRFs, paper mills, and other recyclers that would process them at end-of-use.
From 480 innovative ideas to live prototyping to preparing for pilot readiness and beyond, these next generation cups are paving the way for a waste-free future. These are not solutions that will be ready overnight and require multiple layers of testing and iteration. That’s why NextGen Cup has a multi-stage, multi-year approach to identifying, testing, and scaling sustainable cup solutions to integrate into the global supply chain.
NextGen Cup is designed to both acknowledge the complex journey of the cup, from design through to cup recovery after-use, and accelerate it by de-risking the process in its collective efforts and creating methods for effective prototyping and pilot readiness.
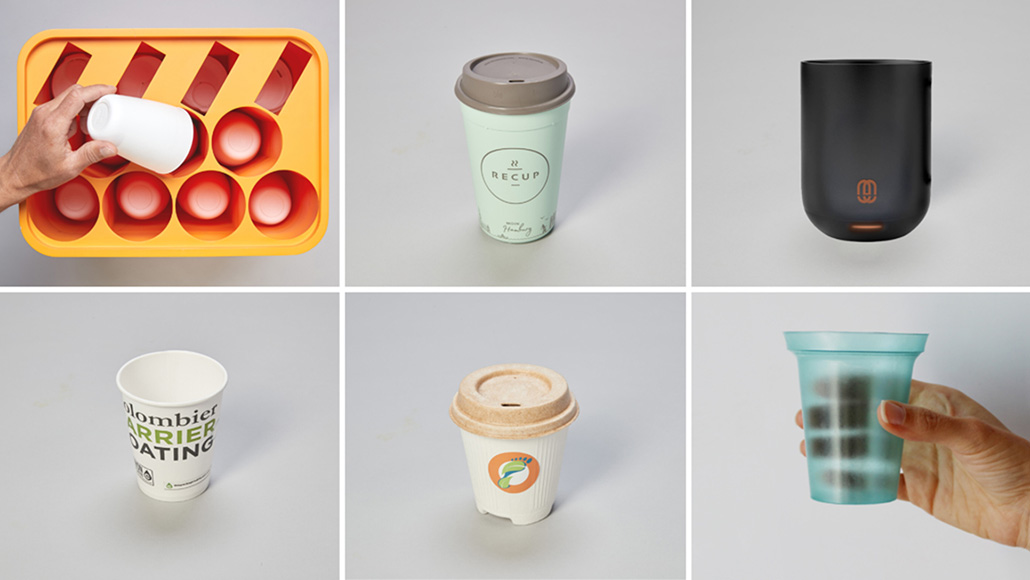
Six Companies Graduate from the NextGen Circular Business Accelerator Ready to Scale Their Sustainable Cup Solutions

The NextGen Consortium, a pre-competitive collaboration managed by Closed Loop Partners in partnership with Starbucks and McDonald’s, accelerates towards a more circular cup system.
Contact: [email protected]
September 25 – NextGen Consortium Partners, investors, and other stakeholders convened during Climate Week in New York City for a Demo Day in which six participants in the NextGen Circular Business Accelerator showcased their manufacture-ready prototypes and pitch-ready business plans for growing their sustainable cup solutions.
The Accelerator follows Closed Loop Partners’ announcement of 12 NextGen Cup Challenge winners in February 2019. Six winning teams entered the NextGen Circular Business Accelerator, launched in partnership with global design firm IDEO to help companies further refine their cup solutions through rapid learning and iteration. The diverse solutions include cutting-edge plant-based materials, new innovative liners for cups, and reusable cup systems that redesign the fiber to-go cup so that it is more widely recoverable or remains in circulation for multiple uses. The six teams participating in the Accelerator are Colombier, CupClub, Footprint, Muuse, RECUP, and SoluBlue.
During the rigorous, six-month Accelerator program, companies accelerated their learnings through live in-context prototyping across four distinct Google campus locations, each housing multiple cafes. Progress for each cup solution was measured across four key categories: customer experience, server experience, performance, and disposal. Companies were able to see first-hand how customers and servers interact with their cups in a restaurant-like environment, capturing real-time feedback in a low-risk setting and identifying areas for refinement.
Companies also visited materials recovery facilities and explored the recovery side of the cup value chain, learning about the systems and infrastructure in place to ensure that their solutions are in alignment. Additionally, companies studied the value of materials recovered post-processing of their cups in order to make the economic case for more circular approaches.
Throughout the Accelerator, companies gained invaluable feedback through direct engagement with NextGen Consortium Partners, including founding partners Starbucks and McDonald’s, supporting partners The Coca-Cola Company, Yum! Brands, Nestlé, and Wendy’s, advisory partner WWF, and innovation partner IDEO. Feedback included insight into what it would take to roll out their solutions at a large scale.
“We are proud of the NextGen collaboration underway with so many companies championing greener cup technologies. We applaud Closed Loop Partners’ continued, on-track progress to determine what’s most viable, and we are excited for our own customers to try greener cups in our stores in the near future.”
John Kelly, senior vice president, Global Public Affairs & Social Impact at Starbucks
The companies were also welcomed behind the scenes of a McDonald’s restaurant to better understand how cups work within a store’s layout and staff operations.
“We were thrilled to have participants in the NextGen Circular Business Accelerator experience. Having these next gen solutions in our restaurants to see first-hand how our crew members manage through our restaurant operations is an important step. Compatibility with the fast pace of a QSR setting is critical, and it was great to see Accelerator teams jump at the opportunity to better understand these in-restaurant conditions. These cup solutions are helping shape the future of packaging, and we want to set them up for success while keeping valuable materials in circulation and, importantly, out of landfills and our oceans.”
Marion Gross, Senior Vice President and Chief Supply Chain Officer, McDonald’s USA
“Seeing how far participants in the NextGen Circular Business Accelerator have come is truly rewarding. The NextGen Consortium will continue to work with winning teams to ensure that when their solutions do enter market at scale they’re set up for success and recoverability.“
Kate Daly, Managing Director of the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners
The other six winners of the NextGen Cup Challenge, which are later-stage in their development, are working with the NextGen Consortium to identify in-market piloting opportunities in regions across the globe. Some participants in the NextGen Circular Business Accelerator are also expected to announce in-store pilots as early as 2020.
The Cup Challenge and the NextGen Circular Business Accelerator are just one part of the NextGen Consortium’s efforts to address single-use food packaging waste globally by advancing the design, commercialization, and recovery of food packaging alternatives. The Consortium is also focused on infrastructure and consumer engagement, supported by stakeholder collaboration across the value chain.
“Watching the aggregation of innovative ideas turn into real progress has been exciting to watch. Now we’ll look to the members of the NextGen Consortium to take these solutions into the marketplace and watch real change happen.”
Erin Simon, Director, Sustainability R&D, World Wildlife Fund
About NextGen
Each year, an estimated 250 billion fiber to-go cups are distributed worldwide. Most of these are not recyclable or compostable. The NextGen Consortium and Cup Challenge launched in 2018 to bring together entrepreneurs, industry, and recyclers to identify and commercialize the next generation of recyclable and/or compostable cups. Closed Loop Partners, Starbucks, McDonald’s, The Coca-Cola Company, Yum! Brands, Nestlé and Wendy’s invite the industry to join this effort to identify a global solution to this shared challenge.
About Closed Loop Partners
Closed Loop Partners is an investment firm that invests in sustainable consumer goods, recycling, and the development of the circular economy. Investors include many of the world’s largest consumer goods companies and family offices interested in investments that provide strong financial returns and tangible social impact. In 2018, Closed Loop Partners launched the Center for the Circular Economy, a New York City-based collaboration center for innovators to commercialize products, services, and technologies that are leading the transition from a linear take, make, waste economy to a restorative one in which materials are shared, re-used, and continuously cycled. Learn more at www.closedlooppartners.com.
About McDonald’s
McDonald’s is the world’s leading global foodservice retailer with over 37,000 locations in over 100 countries. Over 90 percent of McDonald’s restaurants worldwide are owned and operated by independent local business men and women. This year McDonald’s announced a series of commitments demonstrating how it will use its Scale for Good to positively impact the planet and the communities it serves. You can read more about McDonald’s Scale for Good initiatives here.
About Starbucks
Since 1971, Starbucks Coffee Company has been committed to ethically sourcing and roasting high-quality arabica coffee. Today, with stores around the globe, the company is the premier roaster and retailer of specialty coffee in the world. Through our unwavering commitment to excellence and our guiding principles, we bring the unique Starbucks Experience to life for every customer through every cup. To share in the experience, please visit us in our stores or online at http://news.starbucks.com or www.starbucks.com.
NextGen Consortium Partners

