How AI Could Change the Way We Think About Recycling
September 11, 2023
Closed Loop Partners’ Center for the Circular Economy and the NextGen Consortium launch a new study with AI technology company Greyparrot to analyze the composition of polypropylene in recycling streams
Behind the walls of recycling facilities across the U.S., a sea of materials moves through hands and machines working hard to get them to the end of the line––and the beginning of their next life. A critical balance of manual labor and automation enables the sorting and recovery of these materials in a closed loop system. Yet despite a multi-step sortation process, it is difficult to track what flows through the system at all times. It’s a challenge that results in many recycled materials losing potential value, in addition to millions of dollars worth of valuable material being sent to landfill unintentionally.
Among the diverse materials flowing through the recycling system are the yogurt containers, and iced coffee and fountain beverage cups many of us use on a regular basis. These are just a few examples of products made of one of the most commonly used resins in foodservice packaging today: polypropylene (PP). PP is a valuable material that should be kept in circulation to reduce waste and meet corporate commitments to use more recycled content in foodservice packaging. With that said, very little mechanically recycled food-grade PP actually cycles back into food-grade applications. Most end up in nonfood-grade applications that limit their value and the number of times they can be reused. To create a more circular path for food-grade PP, we must first answer the question: what is in the PP stream today, and how much of it is food-grade or clear food-grade PP?
The NextGen Consortium is a multi-year industry collaboration addressing single-use foodservice packaging waste by advancing solutions across material innovation, reuse and recovery infrastructure––and it’s working to answer that question. In the fall of 2022, the Consortium partnered with Resource Recycling Systems to examine PP bales in two materials recovery facilities (MRFs) to learn what was inside. While only a snapshot in time, the results were enlightening.
On average, nearly half of the PP bales (48%) were presumed food-grade, and more than a quarter of the bales were clear food-grade (26%). Clear beverage cups represented 14% of the bale on average. The high percentage of food-grade PP suggested that there is untapped value in the PP stream. A better system is required to ensure food-grade and/or clear food-grade PP is properly sorted into a separate bale at some point in the value chain if we are to retain its highest potential value.
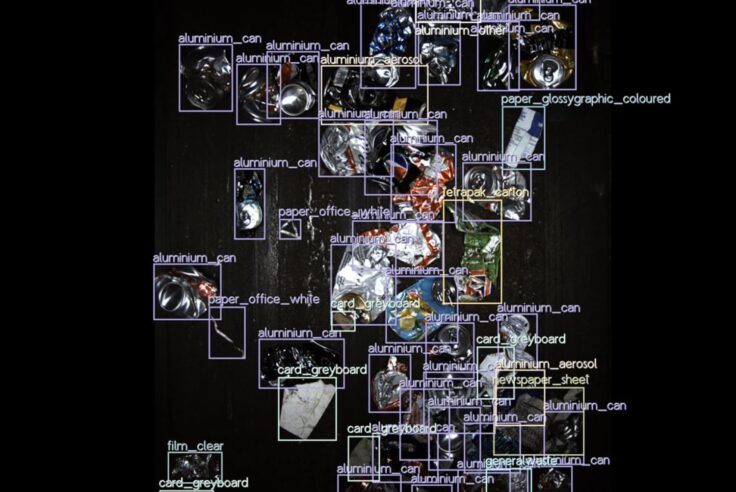
This year, the NextGen Consortium is diving even deeper, launching a first-of-its-kind study leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) to analyze the composition of the PP material stream well before it ends up in a bale. Together with its managing partner––Closed Loop Partners’ Center for the Circular Economy––the NextGen Consortium is working with Greyparrot, a leading AI waste analytics platform for the circular economy. The collaboration aims to track and categorize objects in the PP stream, and determine the volume of valuable food-grade material passing through the system. AI is on the rise as one potential means of increasing visibility into the recycling process. Today, more technologies are needed to handle an increasingly mixed stream of collected materials, including plastics, electronics, textiles and food scraps––and to enable the recovery of clean, high-quality materials.
“Ensuring that recovery infrastructure can keep pace with a rapidly growing and diverse material stream is critical to advancing the circular economy, alongside solutions such as material innovation, reduction and reuse,” said Kate Daly, Managing Director and Head of the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners. “An important part of our work in the NextGen Consortium is identifying opportunities for data collection and analysis that can advance the circularity of foodservice packaging, and drive greater value for stakeholders across the system, including brands, innovators, infrastructure operators and consumers.”
As part of this project, the Greyparrot Analyser units will be installed above the PP recovery conveyor belts at four leading U.S. MRFs: Balcones Recycling, TX; Cougles Recycling, PA; Rumpke Recycling, OH; and Eureka Recycling, MN. Greyparrot’s AI-powered computer vision system uses cameras to capture images of objects in the PP stream, aiming to quantify and qualify the materials flowing through the MRFs. Their AI model will look to categorize each object based on material, format, financial value and brand, as well as distinguish food- and nonfood-grade material, using those images. Their units will then send that data to an analytics dashboard in real-time. Through machine learning, the flexible vision systems can help improve their package recognition and classification over time.
“We use artificial intelligence to gain continuous and reliable visibility into recycling streams,” said Ambarish Mitra, Co-founder and CPO of Greyparrot. “This helps us improve recycling operations by placing waste intelligence into the hands of the people who are recovering, redesigning and remanufacturing the objects we throw away. We are thrilled to work with our U.S. partners towards our vision of a future where every piece of waste is valued as a resource.”
The collaborative project––a first of its kind in North America––will run for more than six months. During that period, it will gather data on the composition of PP bales over time, while accounting for seasonality. That insight can help determine the potential untapped value in these streams, and identify other materials that might be coming through unintentionally. This data can also help shed light on the presumed volume of food-grade material being captured in the system, along with opportunities for recovery and separation into distinct value chains. More broadly, this can advance a circular economy for valuable materials, improve material quality delivered to recycling facilities, and enhance the value of recyclable commodities shipped to U.S. end markets.
“A lot is unknown about the curbside polypropylene stream today. Filling these knowledge gaps can increase the pace of development for material recovery. Understanding the composition of the stream in a large-scale study highlights potential, reduces risk for pioneers and accelerates better design implementation. This study will be the catalyst to developing much larger-scale recycling of polypropylene,” said Curt Cozart, President of Common Sense Solutions and Technical Advisor to the project.
PP cup recovery––alongside material innovation, reuse and fiber cup recovery––is a critical focus for the NextGen Consortium. According to The Recycling Partnership, more than 2 billion pounds of PP are generated every year by single-family households in the U.S. If just 30% of this material were recovered, it would reduce greenhouse gas emissions by over 300,000 metric tons, providing over 600 million pounds of valuable raw material to companies with recycled content commitments for their foodservice packaging, both voluntary and mandated.
The NextGen Consortium has been actively involved in PP recovery since 2021, when it joined The Recycling Partnership’s Polypropylene Recycling Coalition as a Steering Committee member. Through this initiative, the group helps to fund equipment grants for MRFs so that they can effectively capture PP packaging, and improve community recycling access rates. In addition to improving recycling access, the NextGen Consortium is committed to driving recycling rates by supporting the recovery of post-consumer recycled content (PCR) that can be re-incorporated into packaging.
This collaboration with Greyparrot and MRFs across the U.S. is one critical step toward achieving the NextGen Consortium’s goals. As more data about the PP material stream is captured over the next six months, the Consortium will analyze the new data, identifying opportunities to improve PP sortation and recovery into higher value, new food-grade applications and areas where more research is needed. The NextGen Consortium continues to invite additional MRFs to participate in the project, to gain a better understanding into what is flowing through their material streams and identify ways to drive more value to the system.
About the NextGen Consortium
The NextGen Consortium is a multi-year consortium that addresses single-use food packaging waste globally by advancing the design, commercialization, and recovery of food packaging alternatives. The NextGen Consortium is managed by Closed Loop Partners’ Center for the Circular Economy. Starbucks and McDonald’s are the founding partners of the Consortium, with The Coca-Cola Company and PepsiCo as sector lead partners. JDE Peet’s, Wendy’s and Yum! Brands are supporting partners. The World Wildlife Fund (WWF) is the environmental advisory partner. Learn more at www.nextgenconsortium.com.
About the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners
Closed Loop Partners is at the forefront of building the circular economy. The company is comprised of three key business segments: Closed Loop Capital Management, the Center for the Circular Economy and Circular Services. In 2018, Closed Loop Partners launched its innovation center, the Center for the Circular Economy, which unites competitors to tackle complex material challenges and to implement systemic change that advances the circular economy. Closed Loop Partners brings together designers, manufacturers, recovery systems operators, trade organizations, municipalities, policymakers and NGOs to create, invest in, and support scalable innovations that target big system problems. Learn more about the Center’s work here.
Related posts
Press Release
New Data Reveals High Quantities of Food-Grade Polypropylene...
Closed Loop Partners’ Center for the Circular Economy...

Blog Post
Keeping Compost Clean: Tools to Help Reduce Contamination...
The Composting Consortium interviews EcoProducts to...

Press Release
Closed Loop Partners and U.S. Plastics Pact Identify...
Packaging types primed for reuse lay the groundwork...

Blog Post
Why We Invested in Mycocycle: Nature-Inspired Circular...
Closed Loop Partners’ Ventures Group saw a key opportunity...

Press Release
Groundbreaking Results From Citywide Petaluma Reuse...
The Petaluma Reusable Cup Project from the NextGen...

Press Release
Closed Loop Partners’ Portfolio Company, Sage Sustainable...
The bolt-on acquisition scales Sage’s end-to-end...

Press Release
Closed Loop Partners Unveils Groundbreaking Findings...
Closed Loop Partners’ Center for the Circular Economy...

Press Release
Capricorn Investment Group Backs Closed Loop Partners...
The partnership signals tailwinds behind the circular...

Blog Post
8 Tips to Navigate Life Cycle Assessments for Circular...
Closed Loop Partners’ Center for the Circular Economy...

Press Release
Closed Loop Partners Leads $4M Seed Round for LAIIER,...
Investment in the innovative liquid leak detection...

Blog Post
The Key to a Strong Local Economy? It Must Be Circular.
4 ways the circular economy unlocks local value.

Blog Post
Why More Composters Are Recovering Food Scraps and...
Black Earth Compost and Glacial Ridge Composting Facility...
