Why We Invested in Aerflo: Making Reuse an Everyday Norm
September 12, 2024
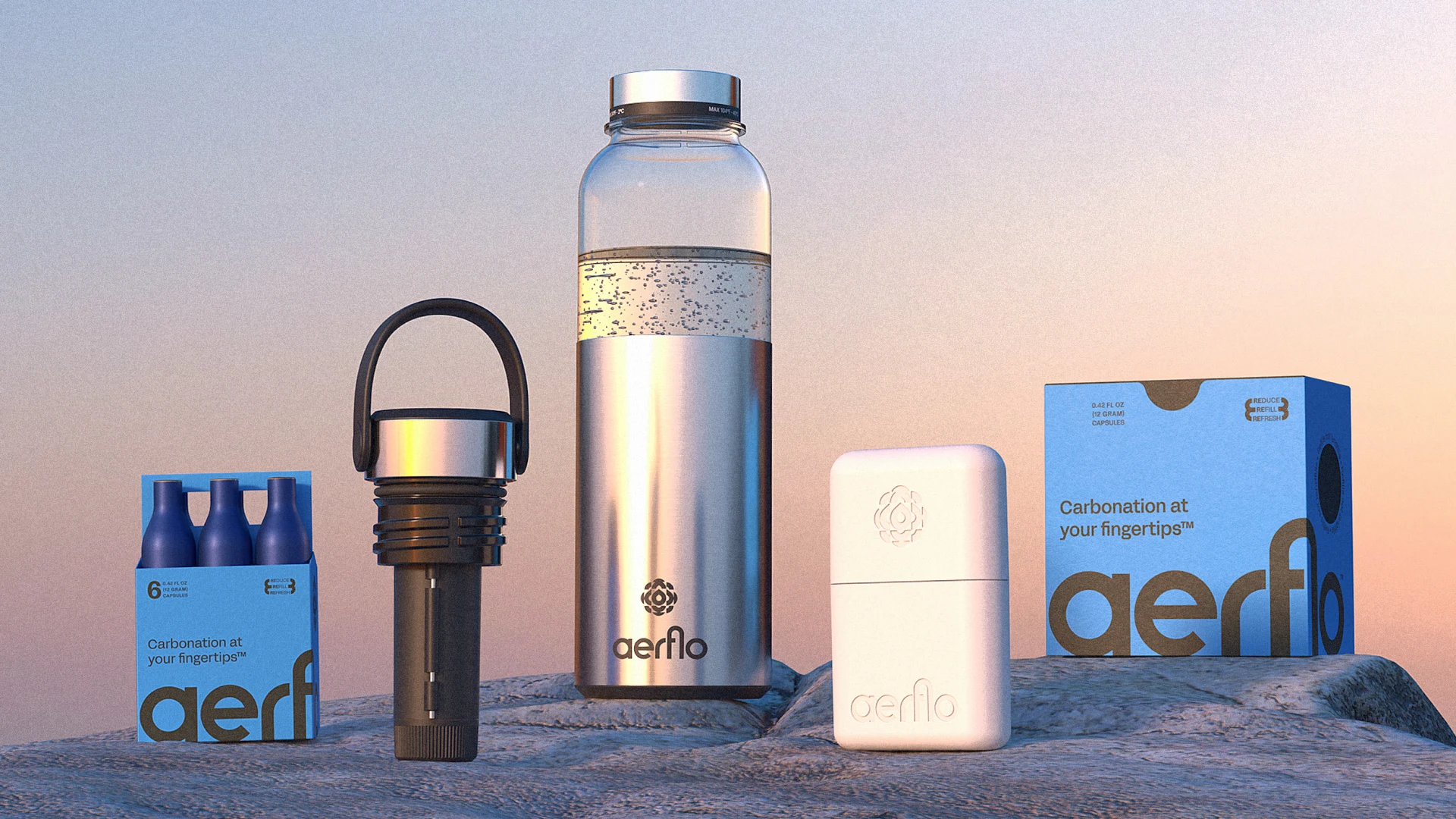

Photo Credit: Fast Company
At this point, we know that reuse is a critical part of the circular economy. It keeps valuable materials in circulation longer, and is part of an essential suite of solutions that also includes upstream material reduction and downstream recovery solutions.
Over the last decade, the use of reusable water bottles in particular has grown––many of us are familiar with the ubiquitous airport water fountains––but broader options for refill remain somewhat underwhelming. It’s, in a word, still.
Many circular reuse models today are appealing to environmentally driven consumers. While this is a growing demographic, it is still not scaled. The question remains: how do we get reuse into the mainstream? How do we get it to, in a word, sparkle?
To gain mainstream traction and drive a shift, solutions need to be better without compromise. Along with environmental benefits, they need to be more delightful and cost less to the end consumer.
Enter Aerflo. John Thorp and Buzz Wiggins, co-founders of Aerflo, started on this journey as outdoor adventurers frustrated that the beverages they wanted to drink only came in single-use, disposable packaging. Together, they embarked on building a solution that would make it possible to enjoy these beverages without waste and create a user experience that catered to the on-the-go lifestyle––all driven by a circular model.
Demand for sparkling water is on the rise in the U.S., with the market anticipated to grow at a compound annual growth rate of over 12% from 2023 to 2032. Today, we are not only seeing a diversity of options on retail shelves, but also a wave of innovations making it possible for consumers to make their own sparkling water. We have seen the growth of at-home countertop devices, such as Soda Stream and Aarke, and in-office spaces with Bevi, introducing a shift away from single-use packaging. But for consumers who want sparkling water on the go, single use has been the only option.
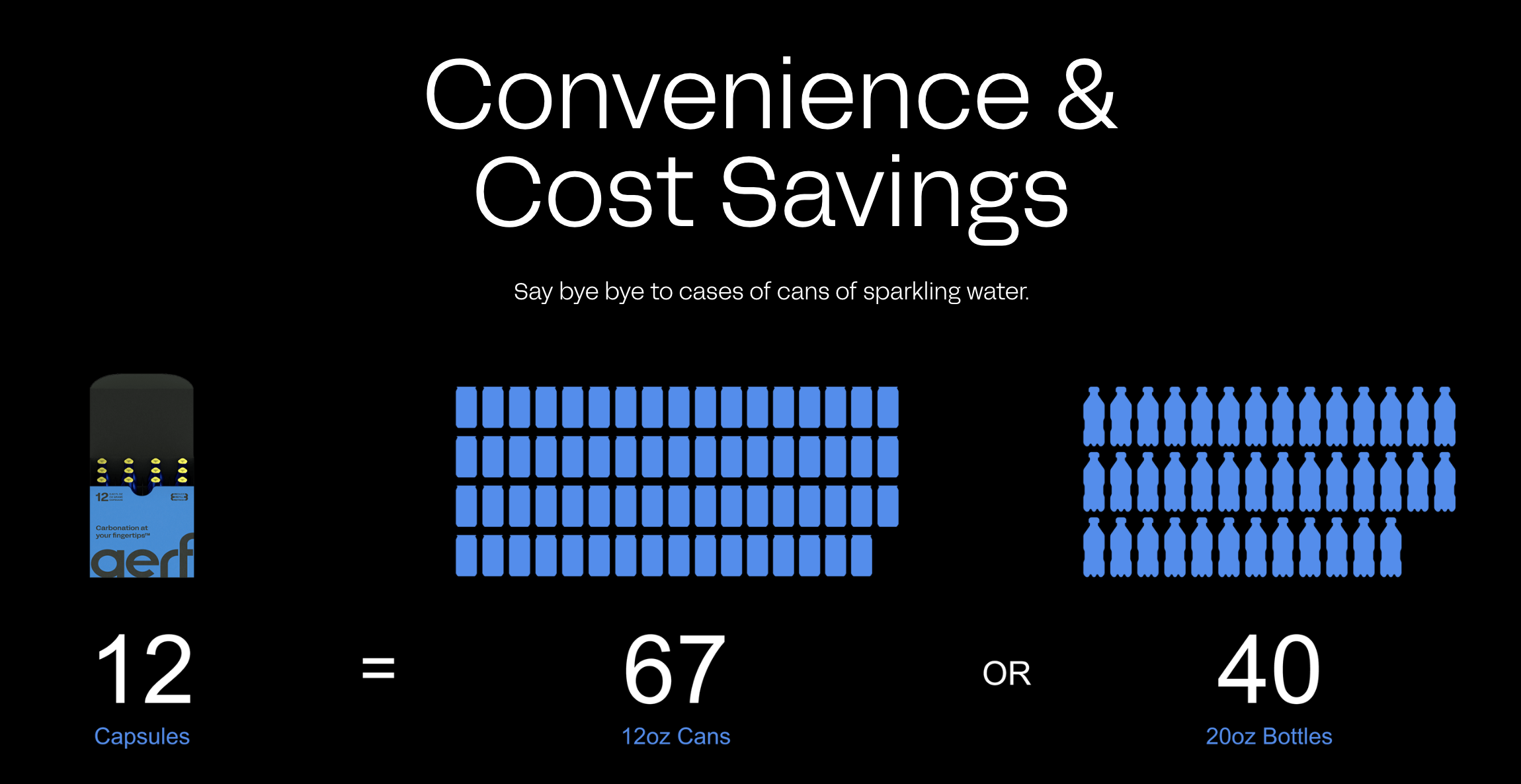
After years of building, John and Buzz launched Aerflo with the first-of-its-kind portable Aerflo Aer1 System that can turn any drinkable water source into refreshing sparkling water with the press of a button. The bottle houses a carbon capsule that can carbonate four full bottles of water. It is designed so that users can see carbonation happen, to gauge how much sparkle to add. The small bubbles mimic those in sparkling water sold in stores, bringing sparkling water to consumers without the need to ship glass bottles or cans filled with water thousands of miles. By inspiring and enabling reuse, Aerflo helps reduce waste and greenhouse gas emissions.
John and Buzz started with the concept of bubbles-on-the-go. How delightful would it be to add bubbles to beverages anywhere in the world, elevating the experience of drinking water, whether someone was on top of a mountain or running through New York City?
Every detail was carefully considered and crafted, ensuring that convenience and taste were not compromised for circularity––a critical factor to the success of reuse.
When capsules are empty, customers ship them back to Aerflo (in the same packaging, and with a return label pre-affixed). This immediately triggers the customer’s next order to be sent––so no subscription is needed. In the company’s fully automated, circular refill facility in New Jersey, the returned Aerflo capsules are cleaned, inspected and refilled before being shipped out to the next customer.

The model is entirely circular. Aside from the clear environmental benefits (each capsule can prevent the need for 330+ cans in its lifetime) this system drives cost savings for customers (60%+ less than single use) and gives the option of still or sparkling at any moment.
Over the past decade, Closed Loop Partners has reviewed hundreds of reuse models through our Closed Loop Ventures Group; we have also tested reuse models in-field and conducted reuse research through our Center for the Circular Economy. And now, Closed Loop Ventures Group is thrilled to announce our investment in Aerflo, a company offering what we believe is a natural choice for on-the-go consumers looking for an elevated experience. Aerflo drinkers don’t need a subscription or commitment and the company offers better value: it is less expensive on a per liter basis than buying carbonated bottled water and offers a more delightful experience to aerate water anywhere, helping make reuse an everyday habit.
About Closed Loop Ventures Group at Closed Loop Partners
Closed Loop Partners has been a leader in the reuse movement for almost a decade. Today, we are actively catalyzing the shift to reuse through our investments and in-market tests––unlocking critical insights and supporting reuse solutions in the field to prepare them for scale. From years of in-field testing and deep research, we have proven that to build successful reuse systems, we need to make reuse a natural choice.
Closed Loop Partners is at the forefront of building the circular economy. The company is comprised of three key business segments: its investment arm, Closed Loop Capital Management; its innovation center, the Center for the Circular Economy; and its operating group, Closed Loop Builders. Closed Loop Capital Management manages venture capital, buyout private equity and catalytic private credit investment strategies. The firm’s venture capital group, the Closed Loop Ventures Group, has been investing early-stage capital into companies developing breakthrough solutions for the circular economy since 2016. The Closed Loop Ventures Group’s portfolio includes companies developing leading innovations in material science, robotics, agritech, sustainable consumer products and advanced technologies that further the circular economy. Closed Loop Partners is based in New York City and is a registered B Corp.
About Aerflo
To learn more, visit https://aerflo.co/.
Disclaimer
This publication is for informational purposes only, and nothing contained herein constitutes an offer to sell or a solicitation of an offer to buy any interest in any investment vehicle managed by Closed Loop Capital Management or any company in which Closed Loop Capital Management or its affiliates have invested. An offer or solicitation will be made only through a final private placement memorandum, subscription agreement and other related documents with respect to a particular investment opportunity and will be subject to the terms and conditions contained in such documents, including the qualifications necessary to become an investor. Closed Loop Capital Management does not utilize its website to provide investment or other advice, and nothing contained herein constitutes a comprehensive or complete statement of the matters discussed or the law relating thereto. Information provided reflects Closed Loop Capital Management’s views as of a particular time and are subject to change without notice. You should obtain relevant and specific professional advice before making any investment decision. Certain information on this Website may contain forward-looking statements, which are subject to risks and uncertainties and speak only as of the date on which they are made. The words “believe”, “expect”, “anticipate”, “optimistic”, “intend”, “aim”, “will” or similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements. Closed Loop Capital Management undertakes no obligation to update publicly or revise any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future developments or otherwise. Past performance is not indicative of future results; no representation is being made that any investment or transaction will or is likely to achieve profits or losses similar to those achieved in the past, or that significant losses will be avoided.
How Can U.S. Composting Scale? Composting Consortium Launches New Report and Platforms to Partner With Composters and Municipalities to Scale Organics Infrastructure Across the U.S.
August 07, 2024
Municipalities and composters play a critical role in developing robust composting infrastructure and collection programs that divert organics from landfill
NEW YORK, Aug. 7, 2024 — Today, the Composting Consortium, a collaboration managed by the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners, released a new blueprint to guide municipal leaders in zero waste, solid waste and sustainability in establishing and scaling composting infrastructure and organics management programs across the country. How Organics Diversion Can Help Achieve Zero Waste Goals: A Blueprint for Action, co-authored with Eco-Cycle, based in Boulder, Colorado, is an essential guide for municipalities seeking to develop food scraps collection programs and to work with composters to meet zero waste and climate goals. Alongside the release of the blueprint, the Consortium invites U.S. municipalities and composters to join two newly launched platforms that support municipalities and composters in scaling organics infrastructure.
Today, food waste in landfills is a major source of methane, a potent greenhouse gas that significantly contributes to climate change. Diverting food scraps and yard waste through municipal organics programs reduces methane emissions and provides environmental benefits such as improved soil health, water conservation, carbon sequestration, and support for local economies and ecosystems. To support this diversion, the U.S. composting industry is in an early stage of transformation. More composters are looking to accept and process more food waste; approximately 70% of composters who process food also accept and process some format of food-contact compostable packaging, with the understanding that accepting these materials helps bring in more food waste to their facilities. However, only 10% of U.S. households have access to organics recycling through drop-off and curbside organics collection programs, and only 4% of wasted food is sent to composters today.
“Since its launch in 2021, the Composting Consortium has been focused on moving the needle to change that statistic,” said Kate Daly, Managing Director and Head of the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners. “By creating this blueprint, we aim to equip municipal leaders with a basic ‘how-to’ manual to launch or scale successful organics programs that contribute to a zero-waste future, clean organics streams and a thriving composting industry.”
The blueprint, How Organics Diversion Can Help Achieve Zero Waste Goals, offers a clear and actionable framework, including:
- Policy and Program Expansion for Diverting Food Waste: This section does a deep dive into effective strategies for policy development. It explores methods to incentivize resident and business participation, while outlining pathways to maximize food waste diversion from landfills.
- Setting Up Programs and Infrastructure: This section provides a clear roadmap for establishing new organics programs. It details best practices for collection methods, explores various processing options (composting facilities, anaerobic digestion), and offers guidance on navigating the critical process of contracting with composters.
- Communication with Program Participants: Recognizing the importance of resident and business engagement, this section provides a comprehensive communications toolkit. It outlines strategies for educating participants on proper sorting techniques, maximizing program participation and fostering long-term program success.
To thoughtfully scale organics management, key stakeholders must collaborate. This helps ensure that composting programs and infrastructure are developed to meet the diverse needs of stakeholders across the organics value chain––from composters, to cities, residents, businesses and more. Alongside the release of the blueprint, the Composting Consortium is launching two new platforms to engage directly with municipalities and composters across the country to support the scale-up of robust composting infrastructure.
The Composting Consortium’s new Composter Innovator Program aims to bring composters across the U.S. to the table to play an active role in shaping the future of the composting industry on topics like contamination, policy and funding food waste composting infrastructure. The group will take on important questions, including identifying the cost of processing compostable packaging and offering recommendations on how to allocate Extended Producer Responsibility funds to support composting infrastructure development. The Consortium invites composters across the U.S. to sign up for the program and be involved in the growth of composting infrastructure across the U.S.
The Consortium is also launching its Municipal Partner Platform, a free-to-access platform for city officials focused on sustainability, zero waste and waste management. The platform connects officials with leaders nationwide to share and discuss best practices in starting and expanding organics collection and infrastructure programs. Municipalities of all sizes and stages of development are invited to reach out to the Composting Consortium to explore ways the network can help them achieve their goals of diverting food waste from landfills.
More information on the Composter Innovator Program and the Municipal Partner Platform can be found at www.closedlooppartners.com/composting-consortium/
About the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners
Closed Loop Partners is a firm at the forefront of building the circular economy. The company is comprised of three key business segments. Closed Loop Capital Management manages venture capital, buyout and catalytic private credit investment strategies on behalf of global corporations, financial institutions and family offices. Closed Loop Builders is an operating group that incubates, builds and scales circular economy infrastructure and services. The Center for the Circular Economy (‘the Center’) is the innovation arm of Closed Loop Partners. The Center executes research and analytics, unites organizations to tackle complex material challenges and implement systemic change that advances the circular economy. The Center’s expertise spans circularity across the full lifecycle of materials, connecting upstream innovation to downstream recovery infrastructure and end markets.
For more information, please visit www.closedlooppartners.com/the-center/
About the Composting Consortium
The Composting Consortium, managed by the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners, is a multi-year industry collaboration on a mission to build a world where organics are kept in circulation. The Consortium advances composting infrastructure and the recovery and processing of food-contact compostable packaging and food scraps in the U.S., to reduce food waste and mitigate climate impact.
The Consortium brings together leading voices across the composting and compostable packaging value chain––from the world’s leading brands to best-in-class composters running the operations on the ground. Through in-market tests, deep research and industry-wide collaboration, the Consortium is laying the groundwork for a more robust, resilient composting system that can keep food waste and compostable packaging in circulation.
For more information, please visit www.closedlooppartners.com/composting-consortium/
Eureka Recycling Receives Over $10 Million in Financing From Closed Loop Partners With Support From American Beverage and The Recycling Partnership
July 22, 2024
Multi-million-dollar financing will improve recycling infrastructure in Minneapolis-St. Paul Area
MINNEAPOLIS, July 22, 2024 — Today, Eureka Recycling, a nonprofit, mission-based independent regional materials recovery facility (MRF) based in Minneapolis, Minnesota, announced a multi-million-dollar financing round led by Closed Loop Partners’ catalytic private credit arm, the Closed Loop Infrastructure Group, alongside American Beverage and The Recycling Partnership.
“This loan funds key upgrades that bolster our resilience to changes in the recycling material stream and shifts in policy across the U.S.,” said Miriam Holsinger, co-president and COO of Eureka Recycling. “Building on our long-term commitment to quality material, traceability in markets and support for our local community, this new equipment and technology improves our ability to effectively sort recyclables in Minnesota and also prevents environmental deterioration from resource extraction, reduces landfill disposal, and generates economic benefits across the municipalities that we support.”
Since its founding, Eureka has been a best-in-class recycling operator, demonstrating the impact and importance of regional, independent recovery facilities in keeping materials in circulation. Eureka Recycling has maintained strong local support in the Minneapolis-St. Paul area and continues to be a key player in the regional recycling market, processing more than 100,000 tons of materials per year.
The over $10 million loan from Closed Loop Partners’ catalytic capital group includes $3 million from American Beverage and the Minnesota Beverage Association. Alongside the loan, The Recycling Partnership provided a grant to support this project. With key infrastructure upgrades, Eureka Recycling can collect, process and return more valuable materials to supply chains and advance a circular economy in the greater Minneapolis-St. Paul area. This will not only support a cleaner community, but also continue to bring revenue to cities and other customers served by the facility and support local jobs.
“We see immense opportunity to support independent recycling operators that are building the necessary infrastructure for a circular economy in the U.S.,” said Jennifer Louie, Managing Director and Head of the Closed Loop Infrastructure Group at Closed Loop Partners. “Eureka’s work has consistently aligned with Closed Loop Partners’ broader mission to advance the circular economy since our partnership began with them nearly a decade ago. This is Closed Loop Partners’ fourth loan to Eureka Recycling in nearly a decade, supporting the MRF in maintaining its leading position in the region. Closed Loop Partners’ Infrastructure Group, across its Infrastructure, Beverage, Circular Plastics and Local Recycling strategies, will continue to deploy capital into private companies, projects and other recycling-focused nonprofits, such as Eureka Recycling.”
Financing is provided as market dynamics, policy shifts and packaging trends change the composition of materials processed by recycling facilities. Investment in regional recycling infrastructure is necessary to keep up with changing material flows and growing demand for high-quality recycled material. The capital will support additional optical sorters to decrease contamination and increase the quality of recovered materials that can be made into new materials, including mixed paper and old corrugated cardboard, polyethylene terephthalate (PET), aluminum, polyethylene and polypropylene. Once the upgrade is completed in 2025, the new machines are estimated to increase the annual collection of PET and aluminum by 222 and 248 tons, respectively.
“One of our industry’s highest priorities is circularity for our valuable bottles and cans,” said American Beverage President and CEO Kevin Keane. “They are made to be remade, and this investment will help make sure more of this valuable material can once again become a new bottle or can. America’s beverage companies are excited to support these important upgrades for the one million residents Eureka serves.”
“Delivering on the promise of a circular economy requires that we build a better recycling system, and that’s exactly what our support to Eureka Recycling is delivering,” said Cody Marshall, Chief Community Strategy Officer at The Recycling Partnership. “By delivering grant funding and forging new partnerships we are providing critical infrastructure that will increase Minnesota’s 45% recycling rate and expand recycling access across the region. That’s good for the people of Minneapolis-St. Paul and for all of us.”
This is the fourth investment from the unique public-private partnership between Closed Loop Partners’ Infrastructure Group, American Beverage’s Every Bottle Back and The Recycling Partnership. The loans, grants and other investments have strengthened infrastructure nationwide to recover materials at their end-of-life, increasing the volume of quality recycled material to meet growing demand for these materials and commitments toward a waste-free world.
About Eureka Recycling
Eureka Recycling is a nonprofit Zero Waste organization and mission-based recycler in Minneapolis, MN. Through education, policy and advocacy work, and operational excellence, Eureka is dedicated to demonstrating that waste is preventable. Eureka provides recycling collection services to more than 100k Twin Cities metro residents, and at its Materials Recovery Facility (MRF), Eureka sorts approximately 100k tons of single-stream recycling annually, serving residents in the Twin Cities, greater Minnesota, and eastern Wisconsin. Committed to Zero Waste and systemic change, Eureka is a founding member of the Alliance of Mission-Based Recyclers (AMBR) which amplifies its impact, advocating for policies that reduce resource extraction, combat climate change, and support local communities.
About Closed Loop Partners
Closed Loop Partners is at the forefront of building the circular economy. The company is comprised of three key business segments: its investment arm, Closed Loop Capital Management, managing venture capital, buyout private equity and catalytic private credit investment strategies; its innovation center, the Center for the Circular Economy; and its operating group, Closed Loop Builders.
The firm’s catalytic private credit arm, the Closed Loop Infrastructure Group, provides a mix of flexible financing solutions to support a range of circular economy projects, companies, infrastructure and enabling technologies. The Infrastructure Group deploys catalytic capital, which seeks to accelerate and de-risk the development of high-impact projects and companies. Areas of strategic investment include providing below-market rate loans to finance circular infrastructure, providing catalytic financing to increase recovery of hard-to-recycle plastics and PET bottles, and financing and deploying small-scale, modular materials recovery facilities (MRFs) to increase recycling in communities with no or limited access to recycling.
Closed Loop Partners is based in New York City and is a registered B Corp. Learn more at closedlooppartners.com.
About American Beverage
American Beverage is the national trade organization representing the broad spectrum of companies that manufacture and distribute non-alcoholic beverages in the United States. The Every Bottle Back initiative is an integrated and comprehensive initiative by The Coca-Cola Company, Keurig Dr Pepper and PepsiCo designed to improve plastics circularity.
Learn more at www.EveryBottleBack.org.
About The Recycling Partnership
The Recycling Partnership is a purpose-driven organization committed to building a better recycling system, one that delivers the economic and environmental benefits our communities and the hundreds of thousands of people who work throughout the recycling industry deserve. The Recycling Partnership’s team of experts, practitioners, and thought leaders with real-world experience works with its partners to create meaningful change across the recycling system and assist communities, companies, and policymakers in enacting such change. The Recycling Partnership uses its one-of-its-kind National Recycling Database that reaches more than 9,000 U.S. recycling programs and develops practical and innovative resources to address critical gaps in the recycling system. Learn more at recyclingpartnership.org.
The Composting Consortium Identifies Investment Opportunities to Scale Food-Waste Composting Infrastructure and Reduce Waste
July 17, 2024
Today, only 4% of U.S. food waste is diverted to compost sites.
New report from the Composting Consortium provides landscape analysis of existing compost infrastructure and markets, outlines composting business models, and recommends blended finance to scale organics circularity.
July 17, 2024, New York, NY – Today, the Composting Consortium, an industry collaboration to strengthen the composting system in the U.S., managed by Closed Loop Partners’ Center for the Circular Economy, released a new report with investment recommendations to scale composting infrastructure and increase the recovery of food waste. The report, Unleashing the Economic and Environmental Potential for Food Waste Composting in the U.S., developed with investors, policymakers and composters in mind, delves into the compost market and opportunities for public and private capital investment amidst rising landfill costs, federal attention on food waste and organics recycling, and state-wide organic bans.
Food waste composting is on the cusp of major growth as the economic, environmental and social consequences of food waste grow more apparent. Macrotrends include the rising cost of landfilling across the country and mounting attention linking food waste in landfills to methane emissions––a factor in climate change. Corporate and municipal zero waste and food waste policies and climate goals are putting a spotlight on composting––an available solution well suited to divert complex post-consumer food waste with food-contact compostable packaging from landfills, while creating compost to sequester carbon, support healthy soils and contribute to agriculture.
While food waste composting infrastructure has remained stagnant in the U.S. for the last six years, the composting industry stands at a critical juncture. Today, there are ~200 compost facilities in the U.S that process food waste, and another ~2,700 facilities that only process yard trimmings. Many of those ~2,700 facilities have the potential to be retrofitted to accept and process food waste. Food waste composting’s potential for social, environmental and economic benefits is well-established, and many individual food waste compost manufacturers have proven the success of the model. However, scaled operations, particularly for large-scale food waste composting facilities, remain hindered by hyper-local logistics, variable municipal engagement and lack of financing tailored to the business model’s dynamics. Blended financing is needed to support large-scale infrastructure that can handle complex food waste streams like post-consumer food scraps with compostable packaging.
According to the Composting Consortium’s report, public and private capital––a mix of grants and philanthropic funding, patient capital, loans and private equity––can work alongside each other to build large-scale composting facilities while nurturing the growth of smaller, established operators. Each type of capital caters to the needs of a particular region and composting business and addresses critical bottlenecks across the entire composting value chain––from establishing efficient collection programs to fostering the development of next-generation technologies and expanding the demand for compost.
“Since the inception of the Composting Consortium, we identified the need to strengthen U.S. composting infrastructure, particularly those solutions that can accept increasingly large and complex organics streams including post-consumer food scraps and compostable food packaging. Investment, alongside policy and multi-stakeholder collaboration, is critical to achieving this,” says Kate Daly, Managing Director and Head of the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners. “After years of on-the-ground work and industry collaboration, the Consortium has identified opportunities for capital to catalyze scale and impact, and advance progress toward zero waste and climate mitigation goals.”
The Composting Consortium is a critical part of Closed Loop Partners’ decade-long work to build a circular economy across a range of areas, including food and organics. In the last 10 years, the firm has made investments in and conducted research on food waste recovery, including composting and distributed anaerobic digestion, and continues to look toward more opportunities to transition away from emissions-intensive production systems and supply chains that create large amounts of waste.
The composting industry presents a compelling opportunity to generate positive social and environmental impact alongside financial returns. By deploying well-placed private investments, investors can play a pivotal role in scaling the industry and creating a lasting positive financial and impact return. By enacting food waste diversion mandates, providing financial incentives for composting infrastructure and collection programs, and supporting research and development of innovative technologies, federal and state governments can play a critical role in enabling the widespread adoption of composting. By embracing innovation and exploring new market opportunities, the composting industry can further improve operational efficiencies and strengthen the composting system as a whole.
By addressing financing hurdles and fostering a supportive ecosystem through collaboration between composting businesses, municipalities and investors, the U.S. composting industry can further scale to advance a more circular economy for organics, reduce our environmental footprint and build a more sustainable future for generations to come.
Unleashing the Economic and Environmental Potential for Food Waste Composting in the U.S.: A Guide for Investors, Policymakers and the Compost Industry is available for download here.
About the Composting Consortium
The Composting Consortium is a multi-year collaboration to pilot industry-wide solutions and build a roadmap for investment in technologies and infrastructure that enable the recovery of compostable food packaging and food scraps. The Composting Consortium is managed by Closed Loop Partners’ Center for the Circular Economy. Learn more about the Consortium at https://www.closedlooppartners.com/composting-consortium/
About the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners
The Center for the Circular Economy is the innovation arm of Closed Loop Partners, a firm at the forefront of building the circular economy. The Center executes research and analytics, unites organizations to tackle complex material challenges and implements systemic change that advances the circular economy. The Center for the Circular Economy’s expertise spans circularity across the full lifecycle of materials, connecting upstream innovation to downstream recovery infrastructure and end markets. Learn more about the Center for the Circular Economy at https://www.closedlooppartners.com/the-center/
The Petaluma Reusable Cup Project: Starbucks, The Coca-Cola Company, PepsiCo Lead Brands Launching City-Wide Reuse System in California City
July 09, 2024
The collaboration, led by the NextGen Consortium, makes reusable cups the default option in national and local restaurants across the City of Petaluma.
July 9, 2024, Petaluma, CA –– Starbucks, The Coca-Cola Company, PepsiCo, Peet’s Coffee, Yum! Brands and other global and local brands and restaurants are partnering in The Petaluma Reusable Cup Project from the NextGen Consortium, led by the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners, to activate an unprecedented collaboration to drive reuse. Starting August 5, more than 30 restaurants in the City of Petaluma, CA, will swap their single-use cups for to-go reusable cups to all customers at no cost, and widespread return points will also be available across the city. This program marks a significant milestone for reuse, as the first initiative of its kind that makes reusable to-go cups the default option across multiple restaurants in a U.S. city, with the opportunity to drive more customers to reuse and displace hundreds of thousands of single-use cups.
The Petaluma Reusable Cup Project is focused on supporting customers to create return habits, a key factor to the success of reuse. The city-wide initiative is a critical step forward to catalyze and scale reuse systems, building on half a decade of work by the NextGen Consortium––a collaboration managed by the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners, in partnership with many global foodservice brands.
The mix of large national chains, local independent restaurants, convenience stores, community hubs and public locations makes this initiative distinctly powerful in shaping consumer habits and cultural norms. More than 30 restaurants in the City of Petaluma will be participating in the initiative, including Starbucks and licensed Starbucks cafés in Target and in Safeway, owned by Albertsons Companies; Peet’s Coffee; KFC and The Habit Burger Grill, owned by Yum!; Dunkin’; as well as many local cafés and restaurants. The initiative was made possible through extensive public-private collaboration, with support and engagement from the City of Petaluma, Zero Waste Sonoma, Recology, community groups and local businesses.
“It takes an entire community to build the future of reuse that we want to see,” says Michael Kobori, Starbucks chief sustainability officer. “Our environmental promise is core to our business and that’s why we’re working toward a future vision of every Starbucks beverage served in a reusable cup. Together with fellow foodservice brands, local stores and community stakeholders, we’re leading this initiative to help further unlock behavior change toward reusables, making it easy for our customers, and any customer, to choose to reuse and reduce waste.”
Across the U.S., 50 billion single-use cups are purchased and disposed of each year. Most of these cups are used out of a restaurant and disposed of at home, work or school, with an average lifespan of less than one hour before going to waste, according to the Center for the Circular Economy’s research. While reuse is growing quickly, use of personal cups and existing takeaway reusable cup systems still face low adoption or low returns. For reuse to scale responsibly, it’s imperative to create an easy and enjoyable consumer experience that makes it easy for customers to remember to bring their own containers or to return one that was given to them.
“To create a world without packaging waste, we need to ensure that food packaging reuse systems are scaled in a way that creates a positive environmental impact––meeting the current needs of people while driving a cultural shift toward reuse,” says Kate Daly, Managing Director and Head of the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners. “By testing reuse across an entire city in partnership with key stakeholders from the community and industry, we can scale reuse collaboratively through thoughtful experimentation, building a future where reuse is the norm.”
The City of Petaluma, CA, located in the northern Bay Area, was selected for the initiative for many reasons. In this region, businesses and consumers are receptive to adopting reuse, given the policy environment promoting the phase-out of non-recyclable single-use packaging. The city also participated in a returnable cup test at participating Starbucks locations in 2023. The size and dense layout of downtown Petaluma, with its tight cluster of restaurants and local shops within walking distance, and proximity to suburban and rural areas, creates the right conditions for testing a reuse system for to-go cups. Collaboration with local stakeholders has helped adapt the initiative to local policy and infrastructure, identify optimal return points across the city and engage the broader community.
“The City of Petaluma is laying the groundwork to make cup reuse not only an option, but the default,” says Kevin McDonnell, the Mayor of the City of Petaluma. “We have an amazing, engaged community, and we look forward to assisting the success of this program, alongside our local restaurants and participating global brands that service our community.”
“Imagine a neighborhood where all to-go cups are reusable, and returning these cups required no extra steps. By making reusable cups as convenient and accessible as single use, we can offer an alternative for residents when they forget to bring their own cups with them,” says Leslie Lukacs, Executive Director of Zero Waste Sonoma. “Universal accessibility creates the foundation for a cultural shift towards reuse.”
The Petaluma Reusable Cup Project will install more than 60 cup return bins across Petaluma. After use and return, the reusable cups will be collected, washed and recirculated for future uses by participating businesses and customers. Muuse, a winner of the 2018 NextGen Cup innovation challenge, was selected by the NextGen Consortium to manage all servicing and reverse logistics for the initiative.
“Transitioning to returnable packaging systems is a critical part of reducing single-use packaging waste, and we need to focus on supporting the operations behind it. These systems must be thoughtfully and responsibly implemented to ensure we are minimizing our impact of creating more waste in the process,” says Brittany Gamez, COO & Co-Founder of Muuse. “It is through initiatives like this that we can identify what is needed to operationalize shared systems at this level and inform how reuse is implemented at scale.”
The initiative, which runs until November, will collect baseline data that measures customer participation and the environmental impact of offering reusables as the default choice for customers, testing whether the model is operationally viable for scale. Data from the initiative can be leveraged by businesses and regulators to support them as they design new reuse systems and draft well-informed packaging regulations.
This is another key step in the NextGen Consortium’s longstanding work to advance reuse. Since 2018, the NextGen Consortium, its brand partners and the Center for the Circular Economy ecosystem have been at the forefront of the reuse movement. In 2019 and 2020, the NextGen Consortium launched groundbreaking trials in the San Francisco Bay Area to understand how reusable cup programs might operate simultaneously across multiple restaurants, leading to a foundational reuse report. Starbucks, a NextGen founding partner, has launched cup share programs in over 25 markets globally, including saturation trials in California. They also recently became the first national coffee retailer to accept reusable cups for drive-thru and mobile orders, making significant progress to incentivize customers to bring their own cups to stores. The work to advance reuse also extends beyond the cup. In 2023, the Consortium to Reinvent the Retail Bag, also managed by the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners, wrapped its largest returnable bag program, alongside its largest bring your own bag program, in partnership with CVS Health, Target and other leading retailers.
Moving forward, the NextGen Consortium will continue its work and collaboration with stakeholders from across the reuse value chain, from innovators and activists to global brands and policymakers, to effectively scale reuse systems that are better for the environment.
About the NextGen Consortium
The NextGen Consortium is a multi-year consortium that addresses single-use foodservice packaging waste by advancing the design, commercialization and recovery of foodservice packaging alternatives. The NextGen Consortium is managed by Closed Loop Partners’ Center for the Circular Economy. Starbucks and McDonald’s are the founding partners of the Consortium, with The Coca-Cola Company and PepsiCo as sector lead partners. Peet’s Coffee, with its parent company JDE Peet’s, Wendy’s, Yum! Brands, Delta Air Lines and Toast are supporting partners. World Wildlife Fund (WWF) is the environmental advisory partner. Learn more at www.nextgenconsortium.com.
About the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners
The Center for the Circular Economy is the innovation arm of Closed Loop Partners, a firm at the forefront of building the circular economy. The Center executes research and analytics, unites organizations to tackle complex material challenges and implements systemic change that advances the circular economy. The Center for the Circular Economy’s expertise spans circularity across the full lifecycle of materials, connecting upstream innovation to downstream recovery infrastructure and end markets. Learn more about the Center for the Circular Economy at closedlooppartners.com/the-center/
How Businesses Can Spark a Cultural Shift Towards Reduction and Reuse in Foodservice Packaging
June 25, 2024
9% of Americans report bringing their own refillable cup when purchasing their coffee on the go. What needs to be true for that number to increase?
The Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners shares insights on how businesses can align with customers in reducing cup waste, drawing on lessons learned from 90 Bring-Your-Own-Cup (BYOC) initiatives in cafés and restaurants across the U.S.
Read more to learn about our insights.
New Report Spotlights State of Circularity in the U.S. Built Environment, Highlighting Key Opportunities to Reduce Waste
June 12, 2024
Funded by 3M, the latest report from the Closed Loop Foundation puts a spotlight on innovation, policy and partnership trends that can help inspire less wasteful building practices and advance circular outcomes in the U.S.
June 12, 2024, New York, NY — Today, the Closed Loop Foundation released a new industry report, Better Buildings: Key Drivers for Constructing a Circular Built Environment in the U.S. The report, which was researched and written by the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners, shares an overview of fundamental circular economy principles that can be applied to the built environment, illustrated by best practice case studies across the country. These examples showcase where circularity in the built environment is already underway in the U.S.
The man-made structures in which society lives, works and plays has a profound impact on quality of life and well-being. The built environment also bears a tremendous environmental cost, with construction and demolition waste constituting a staggering 30-40% of all globally generated solid waste.[1] Moreover, 30% of materials delivered to building sites are ultimately discarded as waste.[2] Materials that constitute buildings and their construction are also responsible for 11% of global energy related carbon emissions.[3] This report is released as the U.S. construction industry faces urgent waste and climate challenges. Within the U.S. alone, construction and demolition debris represents 600 million tons of waste—over 90% stemming from demolition.[4] In New York City, building materials represent 70% of embodied carbon emissions while construction and demolition debris makes up over 60% of the city’s entire solid waste stream.[5]
Transitioning the built environment away from being developed with linear “take-make-waste” practices into one that embodies circular principles––designing out waste and keeping resources in use––is a huge undertaking. To illustrate what a path forward could look like, this report provides a snapshot of where circular economy principles have been incorporated into the built environment in the U.S. The report identifies three key drivers—innovation, policy, partnerships—with a spotlight on investment. It explores innovative circular concepts and approaches related to design, such as design for deconstruction, healthy materials innovation, data management tools like building information modelling, and end-of-life strategies such as adaptive reuse. It provides an overview of federal, state and city regulations advancing circularity through mandated emissions reduction and waste diversion targets. Finally, it examines various cross-sector collaboration models and financing gaps and opportunities.
“At 3M, we are committed to using science and innovation to improve lives and help solve the world’s biggest challenges, including reducing waste and embracing circularity,” says Michael Stroik, Vice President, Community Relations at 3M. “This report from the Closed Loop Foundation provides critical insights into how we can reimagine the built environment in the U.S. through a circular lens. By spotlighting innovative design approaches, supportive policies, collaborative partnerships and case studies across the U.S, this pulse report highlights circular economy-focused work in the built environment to date, with the hope to inspire and accelerate more work in this area.”
“While the U.S. still lags behind Europe in applying circular economy principles to the built environment, this report spotlights where circularity is already underway as a critical first step to identifying circular strategies for the next generation of buildings,” says Kate Daly, Managing Director of the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners, which researched and drafted the report. “These examples show it is possible to reimagine design processes, construction methodologies and material selections to enhance resource efficiency and catalyze economic growth.”
The report is a call for stakeholders across the building value chain—from architects and developers to policymakers and investors—to champion circularity and usher in a new era of sustainable built environments.
About the Closed Loop Foundation
Based in New York City, the Closed Loop Foundation (CLF) aims to further the research and development needed to build a more circular economy. Since its founding, the Foundation has supported numerous organizations, companies and communities working to reduce food, packaging and plastic waste.
CLF received a grant from 3M to fund and release this body of work, which was prepared by the Center for the Circular Economy, the innovation arm of Closed Loop Partners, a firm focused on building the circular economy. The Center executes research and analytics, unites organizations to tackle complex material challenges and implements systemic change that advances the circular economy.
SOURCES:
[1] Shiran Pallewatta et al., Illinois Sustainable Technology Center, “Reprocessed construction and demolition waste as an adsorbent: An appraisal,” July 15, 2023.
[2] Mohamed Osmani, “Chapter 15 – Construction Waste,” in Waste: A Handbook for Management pages 207-218.
[3] World Green Building Council, “Bringing embodied carbon upfront.”
[4] United States Environmental Protection Agency, “Construction and Demolition Debris: Material-Specific Data.”
[5] NYC EDC, “Circular Design & Construction Guidelines.”
The Opportunity of Catalytic Capital
May 14, 2024

Closed Loop Partners is proud to celebrate 10 years of building the circular economy. This blog is part of a series of insights to mark this milestone, highlighting key advancements over the last decade––and the continued work needed over the next decades to accelerate the transition to the circular economy.
For 10 years, our thesis at Closed Loop Partners has remained consistent. The linear economy of materials management––characterized by extraction, single use and disposal––is inefficient. A more effective system exists: a circular economy, whereby people and businesses are custodians of materials over perpetual life cycles. The circular economy creates new value––a fundamental shift in the way society has managed resources over the last 75 years. But to sustain itself well into the future, circularity must be more profitable than the linear system.
Closed Loop Partners saw the economic, environmental and social opportunity in circularity. It was one of the first investment firms to bring together incumbent and emerging players to collectively accelerate this transition. As the firm enters its tenth year, cross-industry stakeholder participation continues to prove its effectiveness in advancing systemic change. Today, markets are experiencing the momentum driving the acceptance and understanding of circularity. Tailwinds including technological innovation, consumer sentiment, regulatory incentives, net-zero commitments and the need for supply chain resiliency propel the current transition. As the circular economy disrupts the status quo, it also presents investment opportunities, inviting collaboration across unexpected corporate, financial, government and community stakeholders.
The opportunity of the circular economy goes far beyond recycling. It represents full systems change, revamping each point in the supply chain: product design, logistics technology, collection capacity reprocessing and remanufacturing. Industries from consumer package goods (CPG) to food & agriculture, retail, technology, energy and the built environment stand to benefit from more efficient management of materials such as plastics & packaging, organics, textiles and critical minerals. To advance systems change across the product life cycle of different materials, different forms of financing are needed.
Today, Closed Loop Partners manages three primary investment strategies: early-stage venture capital, buyout private equity and private credit and catalytic capital. But 10 years ago, our work started with catalytic capital, to amplify the opportunity of circularity and to crowd traditional investment into the capital gap for the transition. 10 years later, it continues to be a critical piece of the puzzle.
Alongside traditional equity and debt solutions, catalytic capital––defined as flexible financing that prioritizes specific outcomes over prevailing market returns––can send a market signal to direct capital flows. This accelerates the uptake and scale of private businesses, municipal projects and infrastructure that are key contributors to durable, circular operations. For a decade, our catalytic investments, provided by Closed Loop Partners’s Infrastructure Group, have been connecting profit incentives with urgent environmental and social impact outcomes. Backed by global retailers, consumer package goods, technology and material science corporations and foundations such as Walmart, Unilever, Starbucks, PepsiCo, P&G, Microsoft, Keurig Dr Pepper, Kenvue (formerly Johnson & Johnson Consumer Health), Danone, Colgate-Palmolive, The Coca-Cola Company, BlueTriton, Amazon and 3M, these private credit and hybrid investments support innovations, private businesses, municipal projects, equipment upgrades and facility development.
By deploying below-market rate and more flexible financing than would otherwise be available, the Closed Loop Infrastructure Group aims to:
- attract follow-on capital from traditional capital markets
- increase the quality and quantity of recycled material kept in the system
- mitigate greenhouse gas emissions
- create more jobs across communities
- advance corporate strategic goals of integrating circularity into their operations.
As early champions of catalytic capital, Closed Loop Partners has worked with an array of municipalities and private companies to accelerate the transition to a profitable and more sustainable system. 10 years in, we have seen the ability of this financing to catalyze the market, in more ways than one.
- Catalyzing More Capital: rPlanet Earth was founded to provide high-quality recycled PET (rPET) packaging and containers to food, beverage and other CPG companies. Operating under a single roof, it is the world’s first completely vertically integrated manufacturer of multiple high rPET content products (up to 100% rPET), creating a much-needed market for the PET packaging collected from curbside recycling programs across California. rPlanet Earth is committed to providing the lowest carbon footprint packaging and products in the marketplace. In 2018, Closed Loop Partners identified the opportunity to bridge a near term capital gap and send a market signal. Our catalytic group provided a $1.5 million loan. Grants and loans from California’s Department of Resources Recycling and Recovery (CalRecycle), CAEATFA and private debt financing sources also provided alternative financing solutions. Also, one of the four largest banks in the U.S. provided a multi-million-dollar loan to finance the construction of their first facility. Together, this capital, along with substantial equity investments from two prominent funds financed rPlanet Earth’s first plant in Vernon, CA.
- Catalyzing Growth: By 2019, Phoenix, Arizona had risen to the fifth largest metropolis in the United States, resulting in a higher volume of recyclable materials. With a $3 million investment from the Closed Loop Infrastructure Group, the City of Phoenix upgraded its North Gateway materials recovery facility (MRF) to enable greater diversion of plastics from landfill and to improve the quality of baled paper produced. The upgrade also helped to increase the overall tonnage of residential recycled materials processed and recovered by the City’s MRF by over 25% within the two years after investment. The city has established a strong reputation for its commitment to the circular economy and its zero waste plan.
- Catalyzing Scale: In 2022, the Closed Loop Infrastructure Group invested in Greyparrot, a leading AI waste analytics platform for the circular economy. Their AI Waste Recognition System is deployed on moving conveyor belts in sorting facilities globally, with the mission of using AI to significantly improve recycling efficiency and increase resource recovery. Supported by funding, Greyparrot has grown to now identify over 25 billion waste objects each year, with 100+ of its Greyparrot Analyzer Units spread across more than 17 countries, and is working with three of the top eight global waste management companies.
Our future requires an increase in material circularity and urgent climate action. Our work at Closed Loop Partners advances efficient materials management and optimized supply chains in a more profitable, more resilient circular system. There is significant opportunity to transition the over $100 trillion global economy from the incumbent linear economic system characterized by wasted resources and profit leakage, to a more efficient circular economy. The Circularity Gap Report estimates that as of 2023, just 7% of the global economy was circular. There is over 90% of the economy yet to transition across materials including paper, metal, plastic, organics, water, critical minerals and carbon itself, and across industries from CPG to fashion, from technology to transportation, energy to real estate.
The transition to circularity presents trillions of dollars of opportunity. Catalytic capital can spark capital flows and accelerate scale, making the innovations, businesses, municipal projects and infrastructure that are critical to a profitable circular system move faster than they otherwise would. For potential collaborators––corporate, foundation, municipal finance or other institutional capital––that would like to learn more, please get in touch with our team. Join us in accelerating the transition to a market-driven circular economy and, in doing so, build a climate-positive future.
—
*This publication is for informational purposes only, and nothing contained herein constitutes an offer to sell or a solicitation of an offer to buy any interest in any investment vehicle managed by Closed Loop Partners or any company in which Closed Loop Partners or its affiliates have invested. An offer or solicitation will be made only through a final private placement memorandum, subscription agreement and other related documents with respect to a particular investment opportunity and will be subject to the terms and conditions contained in such documents, including the qualifications necessary to become an investor. Information provided reflects Closed Loop Partners’ views as of a particular time and are subject to change without notice. You should obtain relevant and specific professional advice before making any investment decision.
Can Compostable Packaging Recovery Help States Reduce Food Waste and Advance Zero Waste Goals? The Composting Consortium’s Toolkit Offers Policymakers the Resources to Get Started
May 08, 2024
The Composting Consortium provides key insights on developing policy that can help U.S. states meet zero waste goals.
May 8, 2024, New York, NY – In response to the rise of food waste legislation and increasing commitments to zero waste and climate action, the Composting Consortium, managed by the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners, releases The Compost Policy Toolkit. This comprehensive toolkit equips policymakers, regulators, composters, brands and retailers with the insights and tools needed to navigate a complex policy landscape around compostable packaging and keep food out of landfill by diverting food scraps towards composting infrastructure. The Toolkit covers three pressing topics in policy today, including Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR), labeling laws and compost end market expansion.
The Composting Consortium, a multi-year collaborative effort focused on advancing circular solutions for food-contact compostable packaging and scaling composting infrastructure, emphasizes the importance of policy in addressing organic waste and advancing circular outcomes, alongside design innovation and recovery infrastructure.
The Compost Policy Toolkit is released at a critical juncture. In the U.S. today, approximately 24% of landfill is food waste, emitting roughly 55 million metric tons of greenhouse gas emissions—and 58% of fugitive methane emissions—per year. Reducing organic waste is recognized as a critical path to achieving critical climate targets. Compostable packaging is also increasingly seen as a mechanism to divert food scraps away from landfill, and the U.S. composting system is slowly transitioning, with more composting facilities now accepting food scraps and some forms of food-contact compostable packaging. To support this transition, policies must help ensure that new materials––such as compostable packaging––align with available infrastructure and markets, as well as incentivize proactive infrastructure development to ensure that these materials are responsibly processed.
U.S. policy on compostable packaging and organics is at a key inflection point. As awareness grows of the environmental impact of organic waste, more landfill bans and materials recovery policies are being implemented to advance packaging and food recovery. To date, ten U.S. states and several major cities have established organics bans. Four U.S. states—California, Colorado, Maine and Oregon—have adopted EPR laws for packaging, and several others have established study bills to evaluate the opportunity for EPR. There is also increasing attention on the importance of soil health, as seen by the proliferation of healthy soils policies and programs across the U.S. As momentum around policy accelerates, there is critical need to develop robust EPR laws that include food-contact compostable packaging, clear labeling laws that help customers and composters identify compostable packaging, and policies that expand the procurement and application of compost across the country.
The Composting Consortium’s toolkit includes insights on a range of policies that are critical to supporting the composting industry in the U.S. It provides policymakers, regulators, composters, brands and retailers with actionable insights on:
- Optimizing EPR for Composting: This brief explores the role of EPR in building composting infrastructure. It emphasizes the importance of conducting thorough needs assessments that account for composting infrastructure and certified food-contact compostable packaging.
- Clear and Consistent Labeling for Compostable Packaging: This brief shares consumer survey findings, highlighting the need for standardized labeling on compostable packaging to avoid confusion with non-compostable packaging, maximize consumer participation in organics diversion programs and support composters in accepting food-contact compostable packaging at their facilities.
- Policy Considerations for Supporting Compost Procurement: This brief explores strategies for promoting the purchase and use of finished compost to enhance our soils, including model procurement policies, compost application incentives and compost education programs.
The Compost Policy Toolkit is an outcome of the Composting Consortium’s in-depth research on policy, made possible by collaboration with key stakeholders across the composting industry. By outlining these key areas and offering practical recommendations, the toolkit aims to equip policymakers and regulators with the insights and best practices needed to navigate the complexities of compostable packaging and infrastructure development.
“Policy plays an important role in keeping resources in circulation whether for reuse systems or in support of robust recycling and composting infrastructure,” said Kate Daly, Managing Director of the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners. “We believe this Policy Toolkit is a valuable resource that will help accelerate the responsible growth of composting infrastructure and unlock the environmental and economic benefits of a circular organics economy.”
The Compost Policy Toolkit is available for download here.
About the Composting Consortium
The Composting Consortium is a multi-year collaboration to pilot industry-wide solutions and build a roadmap for investment in technologies and infrastructure that enable the recovery of compostable food packaging and food scraps. The Composting Consortium is managed by Closed Loop Partners’ Center for the Circular Economy. Learn more about the Consortium at https://www.closedlooppartners.com/composting-consortium/
About the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners
The Center for the Circular Economy is the innovation arm of Closed Loop Partners, a firm at the forefront of building the circular economy. The Center executes research and analytics, unites organizations to tackle complex material challenges and implements systemic change that advances the circular economy. The Center for the Circular Economy’s expertise spans circularity across the full lifecycle of materials, connecting upstream innovation to downstream recovery infrastructure and end markets. Learn more about the Center for the Circular Economy at https://www.closedlooppartners.com/the-center/
Paper Cup Recycling Hits New Milestone in the U.S. With Increased Cup Acceptance at Over 40 Paper Mills
May 07, 2024
The NextGen Consortium and Foodservice Packaging Institute join forces to help more mills accept cups and reduce waste––with more on the way!
May 7, 2024, New York, NY — Today, the NextGen Consortium, an industry collaboration managed by the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners, joined the Foodservice Packaging Institute (FPI) in announcing a major milestone in paper cup recycling in the U.S. Multiple paper mills, from Georgia to Wisconsin, have announced that they will now accept single-use polyethylene (PE)-coated paper cups in bales of mixed paper or polycoat cartons and aseptic packaging. This brings the total number of North American mills accepting paper cups to more than 40, marking significant progress as demand for recycled fiber content grows in the U.S., amidst increasing sustainability commitments and policy tailwinds. The new mills to accept cups include Newman and Company, Inc., Philadelphia, PA; PaperWorks Industries, Wabash, IN; Resolute Forest Products, Menominee Mill, MI; Greif Mill Group in Austell, GA and Milwaukee, WI, among others listed in FPI’s end market map.
Every year, an estimated 250 billion cups are used globally—the majority of which end up in landfills after a single-use. Historically, paper cups had been deemed ‘unrecyclable’ because of their plastic lining, resulting in low recovery rates and valuable materials ending up in landfill. In recent years, as mills compete for diminishing supplies of newspapers and office paper in the recycling system, there has been growing interest in opportunities to recover material categories that contain high-quality fiber, such as paper cups. Many mills––especially new and retrofitted builds––have undertaken repulpability studies to determine whether they can successfully recover the valuable fiber from coated paper packaging, such as fiber cups, for use in recycled fiber products. Positive outcomes of the studies have led to higher acceptance of fiber cups at mills. According to FPI, the dozens of paper mills that now accept paper cups in mixed paper bales represent more than 75 percent of U.S. mixed paper processing demand.
By accepting recovered paper materials, including cups, and reprocessing them into new products, mills play a pivotal role in advancing the larger paper cup recovery process. As more mills effectively recover fiber from paper cups, cup recycling is incentivized further upstream in materials recovery facilities (MRFs) and communities looking to improve their waste diversion efforts. While only 11 percent of communities in the U.S. officially accept cups in their residential recycling programs today, the increasing number of mills that accept cups signals a greater opportunity to grow cup recycling efforts.
“Alongside advancing reuse and material innovation, strengthening paper cup recovery and recycling is critical to keeping cups from going to waste in landfills,” said Kate Daly, Managing Director of the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners. “Paper mills play a critical role in strengthening end markets for cups. By pulling materials through the system, mills accepting cups can drive increased cup processing in recycling facilities and cup collection in communities. We are thrilled to see cup recovery reach this important milestone in the United States, moving us closer to a waste-free future.”
For several years, the NextGen Consortium and Foodservice Packaging Institute have collaborated to strengthen existing materials recovery and recycling infrastructure to recapture more paper cups. Both organizations have released critical reports and research to guide paper cup recovery and recycling, such as NextGen’s report Closing the Loop on Cups and FPI’s White Paper on the The State of Paper Cup Recycling. While the challenges are significant, collaboration among various stakeholders involved in paper cup recovery can help address its scale and complexity.
“We are thrilled to work with a growing set of mills in their efforts to recover poly-coated paper cups,” says Natha Dempsey, President of FPI. “Reliable and responsible end markets for cups catalyze new opportunities for community partnerships, especially in regions that previously didn’t have the capability to recycle them.”
“The mix of recovered paper we receive has changed dramatically over the last several years, now including much more plastic that we have to separate in the repulping process. Paper cups contain good fiber and are no more difficult to recycle than many of the other prominent packaging categories we see today. We look forward to the value it will bring to our outputs at our mills in Austell, GA and Milwaukee, WI,” said Jeff Hilkert, VP Paperboard Sales of Greif Mill Group.”
In addition to working with the mills that are now accepting cups, the NextGen Consortium and FPI continue to work with several other interested mills to run studies that can help determine the viability of paper cups in their system. Furthermore, they are also working with groups up and down the value chain––including brands, MRFs and communities––to ensure more cups can be recycled, especially where viable and robust end markets exist. This collaborative work is a key step forward in increasing the supply of recycled content to meet growing demand, and reducing the amount of valuable materials being sent to landfill.
About the NextGen Consortium
The NextGen Consortium is a multi-year consortium that addresses single-use food packaging waste by advancing the design, commercialization and recovery of food packaging alternatives. The NextGen Consortium is managed by Closed Loop Partners’ Center for the Circular Economy. Starbucks and McDonald’s are the founding partners of the Consortium, with The Coca-Cola Company and PepsiCo as sector lead partners. JDE Peet’s, Wendy’s and Yum! Brands are supporting partners. The World Wildlife Fund (WWF) is the environmental advisory partner. Learn more at www.nextgenconsortium.com.
About the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners
The Center for the Circular Economy is the innovation arm of Closed Loop Partners, a firm at the forefront of building the circular economy. The Center executes research and analytics, unites organizations to tackle complex material challenges and implements systemic change that advances the circular economy. The Center for the Circular Economy’s expertise spans circularity across the full lifecycle of materials, connecting upstream innovation to downstream recovery infrastructure and end markets. Learn more about the Center for the Circular Economy at closedlooppartners.com/the-center/
About the Foodservice Packaging Institute
Founded in 1933, the Foodservice Packaging Institute is the trade association for the foodservice packaging industry in North America. FPI promotes the value and benefits of foodservice packaging and plays an active role in advancing the recovery of FSP to support the circular economy. The association serves as the industry’s leading authority to educate and influence stakeholders. Members include raw material and machinery suppliers, manufacturers, distributors and purchasers of foodservice packaging. For more information, visit www.FPI.org.
